UMTS: Alive and Well - 4G Americas
UMTS: Alive and Well - 4G Americas
UMTS: Alive and Well - 4G Americas
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
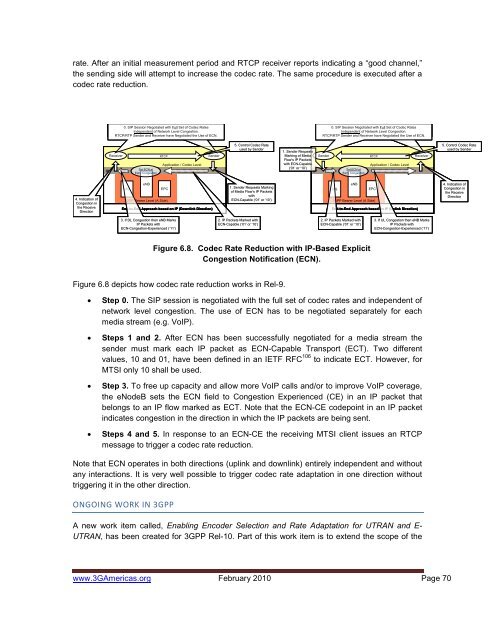
ate. After an initial measurement period <strong>and</strong> RTCP receiver reports indicating a “good channel,”the sending side will attempt to increase the codec rate. The same procedure is executed after acodec rate reduction.0. SIP Session Negotiated with Full Set of Codec RatesIndependent of Network Level Congestion.RTCP/RTP Sender <strong>and</strong> Receiver have Negotiated the Use of ECN.0. SIP Session Negotiated with Full Set of Codec RatesIndependent of Network Level Congestion.RTCP/RTP Sender <strong>and</strong> Receiver have Negotiated the Use of ECN.ReceiverIPRTCPApplication / Codec LevelSet ECN atEarly CongestionSender5. Control Codec Rateused by Sender1. Sender RequestsMarking of MediaSenderFlow’s IP Packetswith ECN-Capable(‘01’ or ‘10’)IPSet ECN atEarly CongestionRTCPApplication / Codec LevelReceiver5. Control Codec Rateused by Sender4. Indication ofCongestion inthe ReceiveDirectioneNBMSEPC3GPP Bearer Level (A Side)End-to-End Approach based on IP (Downlink Direction)1. Sender Requests Markingof Media Flow’s IP PacketswithECN-Capable (‘01’ or ‘10’)eNBMSEPC3GPP Bearer Level (A Side)End-to-End Approach based on IP (Uplink Direction)4. Indication ofCongestion inthe ReceiveDirection3. If DL Congestion then eNB MarksIP Packets withECN-Congestion-Experienced (‘11’)2. IP Packets Marked withECN-Capable (‘01’ or ‘10’)2. IP Packets Marked withECN-Capable (‘01’ or ‘10’)3. If UL Congestion then eNB MarksIP Packets withECN-Congestion-Experienced (‘11’)Figure 6.8. Codec Rate Reduction with IP-Based ExplicitCongestion Notification (ECN).Figure 6.8 depicts how codec rate reduction works in Rel-9.• Step 0. The SIP session is negotiated with the full set of codec rates <strong>and</strong> independent ofnetwork level congestion. The use of ECN has to be negotiated separately for eachmedia stream (e.g. VoIP).• Steps 1 <strong>and</strong> 2. After ECN has been successfully negotiated for a media stream thesender must mark each IP packet as ECN-Capable Transport (ECT). Two differentvalues, 10 <strong>and</strong> 01, have been defined in an IETF RFC 106 to indicate ECT. However, forMTSI only 10 shall be used.• Step 3. To free up capacity <strong>and</strong> allow more VoIP calls <strong>and</strong>/or to improve VoIP coverage,the eNodeB sets the ECN field to Congestion Experienced (CE) in an IP packet thatbelongs to an IP flow marked as ECT. Note that the ECN-CE codepoint in an IP packetindicates congestion in the direction in which the IP packets are being sent.• Steps 4 <strong>and</strong> 5. In response to an ECN-CE the receiving MTSI client issues an RTCPmessage to trigger a codec rate reduction.Note that ECN operates in both directions (uplink <strong>and</strong> downlink) entirely independent <strong>and</strong> withoutany interactions. It is very well possible to trigger codec rate adaptation in one direction withouttriggering it in the other direction.ONGOING WORK IN 3GPPA new work item called, Enabling Encoder Selection <strong>and</strong> Rate Adaptation for UTRAN <strong>and</strong> E-UTRAN, has been created for 3GPP Rel-10. Part of this work item is to extend the scope of thewww.3G<strong>Americas</strong>.org February 2010 Page 70