Diffusion Processes with Hidden States from ... - FU Berlin, FB MI
Diffusion Processes with Hidden States from ... - FU Berlin, FB MI
Diffusion Processes with Hidden States from ... - FU Berlin, FB MI
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
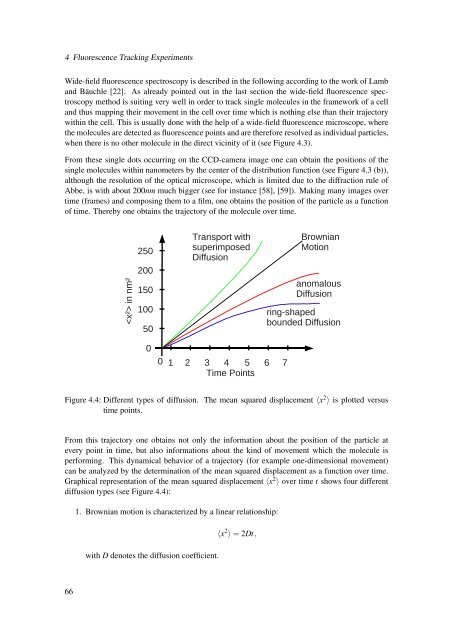
4 Fluorescence Tracking ExperimentsWide-field fluorescence spectroscopy is described in the following according to the work of Lamband Bäuchle [22]. As already pointed out in the last section the wide-field fluorescence spectroscopymethod is suiting very well in order to track single molecules in the framework of a celland thus mapping their movement in the cell over time which is nothing else than their trajectory<strong>with</strong>in the cell. This is usually done <strong>with</strong> the help of a wide-field fluorescence microscope, wherethe molecules are detected as fluorescence points and are therefore resolved as individual particles,when there is no other molecule in the direct vicinity of it (see Figure 4.3).From these single dots occurring on the CCD-camera image one can obtain the positions of thesingle molecules <strong>with</strong>in nanometers by the center of the distribution function (see Figure 4.3 (b)),although the resolution of the optical microscope, which is limited due to the diffraction rule ofAbbe, is <strong>with</strong> about 200nm much bigger (see for instance [58], [59]). Making many images overtime (frames) and composing them to a film, one obtains the position of the particle as a functionof time. Thereby one obtains the trajectory of the molecule over time. in nm²25020015010050Transport <strong>with</strong>superimposed<strong>Diffusion</strong>BrownianMotionanomalous<strong>Diffusion</strong>ring-shapedbounded <strong>Diffusion</strong>001 2 3 4 5 6 7Time PointsFigure 4.4: Different types of diffusion. The mean squared displacement 〈x 2 〉 is plotted versustime points.From this trajectory one obtains not only the information about the position of the particle atevery point in time, but also informations about the kind of movement which the molecule isperforming. This dynamical behavior of a trajectory (for example one-dimensional movement)can be analyzed by the determination of the mean squared displacement as a function over time.Graphical representation of the mean squared displacement 〈x 2 〉 over time t shows four differentdiffusion types (see Figure 4.4):1. Brownian motion is characterized by a linear relationship:<strong>with</strong> D denotes the diffusion coefficient.〈x 2 〉 = 2Dt,66