ICT and e-Business Impact in the Retail Industry - empirica
ICT and e-Business Impact in the Retail Industry - empirica
ICT and e-Business Impact in the Retail Industry - empirica
- No tags were found...
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
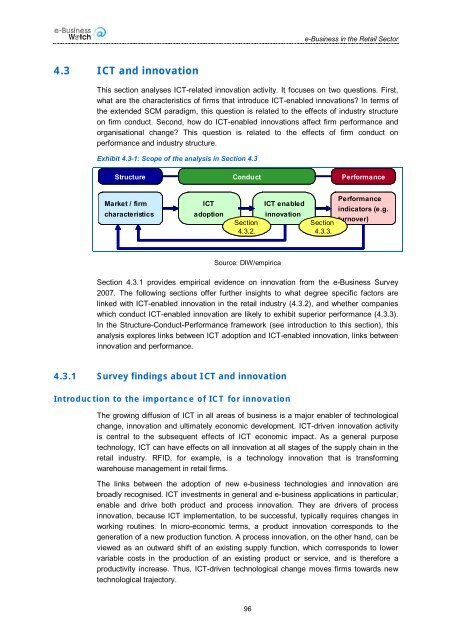
e-<strong>Bus<strong>in</strong>ess</strong> <strong>in</strong> <strong>the</strong> <strong>Retail</strong> Sector4.3 <strong>ICT</strong> <strong>and</strong> <strong>in</strong>novationThis section analyses <strong>ICT</strong>-related <strong>in</strong>novation activity. It focuses on two questions. First,what are <strong>the</strong> characteristics of firms that <strong>in</strong>troduce <strong>ICT</strong>-enabled <strong>in</strong>novations? In terms of<strong>the</strong> extended SCM paradigm, this question is related to <strong>the</strong> effects of <strong>in</strong>dustry structureon firm conduct. Second, how do <strong>ICT</strong>-enabled <strong>in</strong>novations affect firm performance <strong>and</strong>organisational change? This question is related to <strong>the</strong> effects of firm conduct onperformance <strong>and</strong> <strong>in</strong>dustry structure.Exhibit 4.3-1: Scope of <strong>the</strong> analysis <strong>in</strong> Section 4.3Structure Conduct PerformanceMarket / firmcharacteristics<strong>ICT</strong>adoptionSection4.3.2.<strong>ICT</strong> enabled<strong>in</strong>novationSection4.3.3.Performance<strong>in</strong>dicators (e.g.turnover)Source: DIW/<strong>empirica</strong>Section 4.3.1 provides <strong>empirica</strong>l evidence on <strong>in</strong>novation from <strong>the</strong> e-<strong>Bus<strong>in</strong>ess</strong> Survey2007. The follow<strong>in</strong>g sections offer fur<strong>the</strong>r <strong>in</strong>sights to what degree specific factors arel<strong>in</strong>ked with <strong>ICT</strong>-enabled <strong>in</strong>novation <strong>in</strong> <strong>the</strong> retail <strong>in</strong>dustry (4.3.2), <strong>and</strong> whe<strong>the</strong>r companieswhich conduct <strong>ICT</strong>-enabled <strong>in</strong>novation are likely to exhibit superior performance (4.3.3).In <strong>the</strong> Structure-Conduct-Performance framework (see <strong>in</strong>troduction to this section), thisanalysis explores l<strong>in</strong>ks between <strong>ICT</strong> adoption <strong>and</strong> <strong>ICT</strong>-enabled <strong>in</strong>novation, l<strong>in</strong>ks between<strong>in</strong>novation <strong>and</strong> performance.4.3.1 Survey f<strong>in</strong>d<strong>in</strong>gs about <strong>ICT</strong> <strong>and</strong> <strong>in</strong>novationIntroduction to <strong>the</strong> importance of <strong>ICT</strong> for <strong>in</strong>novationThe grow<strong>in</strong>g diffusion of <strong>ICT</strong> <strong>in</strong> all areas of bus<strong>in</strong>ess is a major enabler of technologicalchange, <strong>in</strong>novation <strong>and</strong> ultimately economic development. <strong>ICT</strong>-driven <strong>in</strong>novation activityis central to <strong>the</strong> subsequent effects of <strong>ICT</strong> economic impact. As a general purposetechnology, <strong>ICT</strong> can have effects on all <strong>in</strong>novation at all stages of <strong>the</strong> supply cha<strong>in</strong> <strong>in</strong> <strong>the</strong>retail <strong>in</strong>dustry. RFID, for example, is a technology <strong>in</strong>novation that is transform<strong>in</strong>gwarehouse management <strong>in</strong> retail firms.The l<strong>in</strong>ks between <strong>the</strong> adoption of new e-bus<strong>in</strong>ess technologies <strong>and</strong> <strong>in</strong>novation arebroadly recognised. <strong>ICT</strong> <strong>in</strong>vestments <strong>in</strong> general <strong>and</strong> e-bus<strong>in</strong>ess applications <strong>in</strong> particular,enable <strong>and</strong> drive both product <strong>and</strong> process <strong>in</strong>novation. They are drivers of process<strong>in</strong>novation, because <strong>ICT</strong> implementation, to be successful, typically requires changes <strong>in</strong>work<strong>in</strong>g rout<strong>in</strong>es. In micro-economic terms, a product <strong>in</strong>novation corresponds to <strong>the</strong>generation of a new production function. A process <strong>in</strong>novation, on <strong>the</strong> o<strong>the</strong>r h<strong>and</strong>, can beviewed as an outward shift of an exist<strong>in</strong>g supply function, which corresponds to lowervariable costs <strong>in</strong> <strong>the</strong> production of an exist<strong>in</strong>g product or service, <strong>and</strong> is <strong>the</strong>refore aproductivity <strong>in</strong>crease. Thus, <strong>ICT</strong>-driven technological change moves firms towards newtechnological trajectory.96