Student Flow at Primary Level - DISE
Student Flow at Primary Level - DISE
Student Flow at Primary Level - DISE
- No tags were found...
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
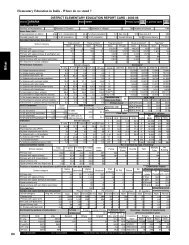
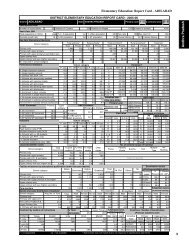
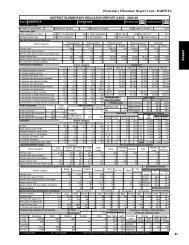
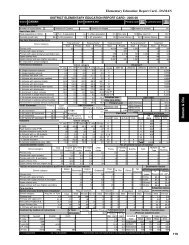
64 <strong>Student</strong> <strong>Flow</strong> <strong>at</strong> <strong>Primary</strong> <strong>Level</strong>Table 33Transition R<strong>at</strong>e <strong>at</strong> <strong>Primary</strong> <strong>Level</strong>: DPEP and Non-DPEPDistricts, 2004-05Sl Non-DPEP Districts DPEP DistrictsNo. St<strong>at</strong>eBoys Girls Total Boys Girls Total1 Andhra Pradesh 89.13 88.06 88.58 88.12 84.50 86.352 Assam 87.27 89.33 88.26 83.74 86.07 84.863 Bihar 63.84 61.68 62.98 66.62 62.99 65.144 Chh<strong>at</strong>tisgarh 128.66 126.67 127.68 102.34 99.16 100.835 Gujar<strong>at</strong> 91.04 90.46 90.78 83.83 83.66 83.756 Haryana 81.72 84.22 82.92 78.25 76.06 77.227 Himachal Pradesh 95.58 95.49 95.53 88.80 84.78 86.888 Jharkhand 82.85 84.84 83.67 93.20 96.91 94.889 Karn<strong>at</strong>aka 85.22 86.89 86.03 72.93 72.11 72.5310 Kerala 93.53 94.97 94.24 98.41 99.79 99.0811 Madhya Pradesh 72.01 74.71 73.27 60.41 57.28 58.9712 Maharashtra 117.09 116.16 116.65 99.64 99.42 99.5313 Orissa 84.18 83.48 83.85 77.36 74.09 75.8614 Rajasthan 96.10 85.71 91.90 101.20 91.28 96.8515 Tamil Nadu 99.87 99.57 99.73 85.13 84.65 84.9016 Uttar Pradesh 80.90 78.37 79.69 65.45 61.62 63.6517 Uttarakhand 84.77 88.17 86.43 83.82 79.27 81.5618 West Bengal 62.40 63.25 62.82 60.86 60.37 60.62All Districts 87.62 87.54 87.58 76.46 73.74 75.19Note: More than 100 transition r<strong>at</strong>e may be because of inconsistent enrolment d<strong>at</strong>a ormigr<strong>at</strong>ion of children into th<strong>at</strong> st<strong>at</strong>e <strong>at</strong> the Grade VI level.Concluding Observ<strong>at</strong>ionsDepending upon the availability of d<strong>at</strong>a, an indic<strong>at</strong>or to measure dropoutr<strong>at</strong>e should be developed. If resources are available, true-cohort studyin which each and every enrolled child is tracked should be undertakenand can be used for assessing the quantum of drop-out as well as thecompletion r<strong>at</strong>es. In case the resources are not available but d<strong>at</strong>a available,retention r<strong>at</strong>e by using enrolment and repe<strong>at</strong>ers d<strong>at</strong>a over a period offive years should only be utilised to assess the retaining capacity of aneduc<strong>at</strong>ion system. The retention r<strong>at</strong>e so obtained is subtracted from 100to obtain drop-out r<strong>at</strong>e for an educ<strong>at</strong>ional level. To know the root causeof low retention r<strong>at</strong>e or high drop-out r<strong>at</strong>e, it is essential th<strong>at</strong> the samebe calcul<strong>at</strong>ed and analysed <strong>at</strong> the disaggreg<strong>at</strong>ed levels and if d<strong>at</strong>a