- Page 3 and 4: For Alexander and SarinaWith all ou
- Page 5 and 6: First edition 1989Second edition fi
- Page 7 and 8: viPrefacepublishers, who I am sure,
- Page 9 and 10: viiiAcknowledgementsFig 6.5 is repr
- Page 11 and 12: Table of Contents1. Cell Membranes,
- Page 13 and 14: xiiContentsGASTRIC pH .............
- Page 15 and 16: xivContents9. Nasal Drug Delivery .
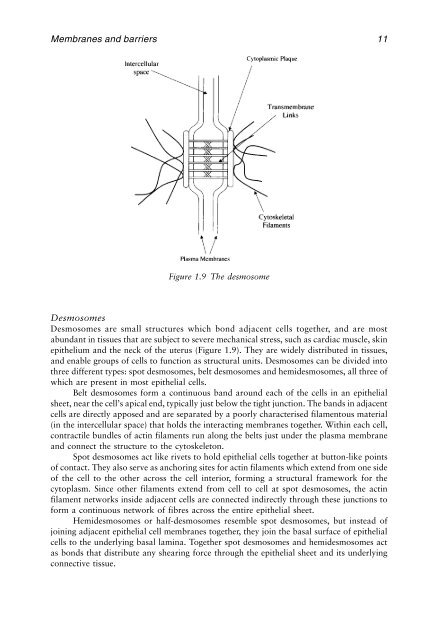
- Page 18 and 19: Chapter OneCell Membranes, Epitheli
- Page 20 and 21: Membranes and barriers 3Figure 1.1
- Page 22 and 23: Membranes and barriers 5Modulation
- Page 24 and 25: Membranes and barriers 7Membrane pr
- Page 26 and 27: Membranes and barriers 9Figure 1.6
- Page 30 and 31: Membranes and barriers 13Figure 1.1
- Page 32 and 33: Membranes and barriers 15Figure 1.1
- Page 34 and 35: Membranes and barriers 17Figure 1.1
- Page 36 and 37: Chapter TwoParenteral Drug Delivery
- Page 38 and 39: Parenteral drug delivery 21Figure 2
- Page 40 and 41: Parenteral drug delivery 23catheter
- Page 42 and 43: Parenteral drug delivery 25Figure 2
- Page 44 and 45: Parenteral drug delivery 27Figure 2
- Page 46 and 47: Parenteral drug delivery 29fluid is
- Page 48 and 49: Parenteral drug delivery 31Figure 2
- Page 50 and 51: Parenteral drug delivery 33Receptor
- Page 52: Parenteral drug delivery 3526. Tsuj
- Page 55 and 56: 38 Physiological PharmaceuticsANATO
- Page 57 and 58: 40 Physiological PharmaceuticsFigur
- Page 59 and 60: 42 Physiological Pharmaceuticsgland
- Page 61 and 62: 44 Physiological PharmaceuticsABSOR
- Page 63 and 64: 46 Physiological PharmaceuticsThe r
- Page 65 and 66: 48 Physiological Pharmaceuticsa) in
- Page 67 and 68: 50 Physiological Pharmaceuticswhen
- Page 69 and 70: 52 Physiological Pharmaceuticsin de
- Page 71 and 72: 54 Physiological PharmaceuticsFigur
- Page 73 and 74: 56 Physiological Pharmaceutics8. We
- Page 75 and 76: 58 Physiological Pharmaceutics59. A
- Page 77 and 78: 60 Physiological PharmaceuticsINTRO
- Page 79 and 80:
62 Physiological PharmaceuticsFigur
- Page 81 and 82:
64 Physiological PharmaceuticsTable
- Page 83 and 84:
66 Physiological Pharmaceuticsliqui
- Page 85 and 86:
68 Physiological PharmaceuticsFigur
- Page 87 and 88:
70 Physiological PharmaceuticsTable
- Page 89 and 90:
72 Physiological Pharmaceutics12. W
- Page 92 and 93:
Chapter FiveThe StomachANATOMY AND
- Page 94 and 95:
The stomach 77Figure 5.2 Structure
- Page 96 and 97:
The stomach 79Gastric glandsThe gas
- Page 98 and 99:
The stomach 81Figure 5.7 Mechanism
- Page 100 and 101:
The stomach 83absorbed from the sto
- Page 102 and 103:
The stomach 85Night-time transient
- Page 104 and 105:
The stomach 87particle size indiges
- Page 106 and 107:
The stomach 89Figure 5.13 MRI cross
- Page 108 and 109:
The stomach 91species and man is po
- Page 110 and 111:
The stomach 93Figure 5.15 The effec
- Page 112 and 113:
The stomach 95emerged from the shel
- Page 114 and 115:
The stomach 97Figure 5.17 The gastr
- Page 116 and 117:
The stomach 99In order to improve b
- Page 118 and 119:
The stomach 101Figure 5.21—Gastri
- Page 120 and 121:
The stomach 103The anatomy and dime
- Page 122 and 123:
The stomach 10533:1283-1290.35. Cun
- Page 124 and 125:
The stomach 10782. Ingani HM, Timme
- Page 126 and 127:
Chapter SixDrug Absorption from the
- Page 128 and 129:
Small intestine 111Figure 6.1 Secti
- Page 130 and 131:
Small intestine 113are uncommon and
- Page 132 and 133:
Small intestine 115underlying tissu
- Page 134 and 135:
Small intestine 117Brief periodic b
- Page 136 and 137:
Small intestine 119is extremely rap
- Page 138 and 139:
Small intestine 121Figure 6.5 Segme
- Page 140 and 141:
Small intestine 123Measurements of
- Page 142 and 143:
Small intestine 125Figure 6.8 Small
- Page 144 and 145:
Small intestine 127Scintigraphy oft
- Page 146 and 147:
Small intestine 129It is known that
- Page 148 and 149:
Small intestine 131It was soon real
- Page 150 and 151:
Small intestine 133colonic absorpti
- Page 152 and 153:
Small intestine 135also transform d
- Page 154 and 155:
Small intestine 137REFERENCES1. Bry
- Page 156 and 157:
Small intestine 13949. Hidalgo IJ,
- Page 158:
Small intestine 14193. Bogentoft C,
- Page 161 and 162:
144 Physiological PharmaceuticsAnti
- Page 163 and 164:
146 Physiological PharmaceuticsFigu
- Page 165 and 166:
148 Physiological Pharmaceuticsto t
- Page 167 and 168:
150 Physiological Pharmaceuticssodi
- Page 169 and 170:
152 Physiological PharmaceuticsOnce
- Page 171 and 172:
154 Physiological PharmaceuticsFigu
- Page 173 and 174:
156 Physiological PharmaceuticsThe
- Page 175 and 176:
158 Physiological PharmaceuticsFigu
- Page 177 and 178:
160 Physiological Pharmaceuticscomp
- Page 179 and 180:
162 Physiological PharmaceuticsThe
- Page 181 and 182:
164 Physiological PharmaceuticsFigu
- Page 183 and 184:
166 Physiological Pharmaceuticsthe
- Page 185 and 186:
168 Physiological PharmaceuticsFigu
- Page 187 and 188:
170 Physiological Pharmaceuticsdemo
- Page 189 and 190:
172 Physiological PharmaceuticsFigu
- Page 191 and 192:
174 Physiological Pharmaceuticsreac
- Page 193 and 194:
176 Physiological Pharmaceutics42.
- Page 195 and 196:
178 Physiological Pharmaceutics89.
- Page 197 and 198:
180 Physiological Pharmaceutics134.
- Page 199 and 200:
182 Physiological PharmaceuticsINTR
- Page 201 and 202:
184 Physiological PharmaceuticsDerm
- Page 203 and 204:
186 Physiological Pharmaceuticsalum
- Page 205 and 206:
188 Physiological Pharmaceuticsand
- Page 207 and 208:
190 Physiological PharmaceuticsFigu
- Page 209 and 210:
192 Physiological Pharmaceuticsmay
- Page 211 and 212:
194 Physiological Pharmaceuticsmemb
- Page 213 and 214:
196 Physiological Pharmaceutics21.
- Page 215 and 216:
198 Physiological Pharmaceutics70.
- Page 217 and 218:
200 Physiological PharmaceuticsANAT
- Page 219 and 220:
202 Physiological Pharmaceuticslowe
- Page 221 and 222:
204 Physiological Pharmaceuticspoin
- Page 223 and 224:
206 Physiological PharmaceuticsSjö
- Page 225 and 226:
208 Physiological PharmaceuticsFigu
- Page 227 and 228:
210 Physiological Pharmaceuticsagon
- Page 229 and 230:
212 Physiological PharmaceuticsMech
- Page 231 and 232:
214 Physiological Pharmaceuticsvivo
- Page 233 and 234:
216 Physiological PharmaceuticsLoca
- Page 235 and 236:
218 Physiological Pharmaceutics26.
- Page 237 and 238:
220 Physiological Pharmaceutics74.
- Page 239 and 240:
222 Physiological PharmaceuticsDRUG
- Page 241 and 242:
224 Physiological PharmaceuticsFigu
- Page 243 and 244:
226 Physiological PharmaceuticsFigu
- Page 245 and 246:
228 Physiological Pharmaceutics2% m
- Page 247 and 248:
230 Physiological Pharmaceuticsis r
- Page 249 and 250:
232 Physiological Pharmaceuticsabno
- Page 251 and 252:
234 Physiological Pharmaceuticsinha
- Page 253 and 254:
236 Physiological Pharmaceuticsprob
- Page 255 and 256:
238 Physiological PharmaceuticsSome
- Page 257 and 258:
240 Physiological PharmaceuticsFigu
- Page 259 and 260:
242 Physiological PharmaceuticsL.mi
- Page 261 and 262:
244 Physiological PharmaceuticsAdre
- Page 263 and 264:
246 Physiological Pharmaceutics9. P
- Page 266 and 267:
Chapter ElevenOcular Drug DeliveryI
- Page 268 and 269:
Ocular drug delivery 251STRUCTURE O
- Page 270 and 271:
Ocular drug delivery 253chamber. It
- Page 272 and 273:
Ocular drug delivery 255The superfi
- Page 274 and 275:
Ocular drug delivery 257Figure 11.7
- Page 276 and 277:
Ocular drug delivery 259Figure 11.9
- Page 278 and 279:
Ocular drug delivery 261Influence o
- Page 280 and 281:
Ocular drug delivery 263SpraysSpray
- Page 282 and 283:
Ocular drug delivery 265endothelial
- Page 284 and 285:
Ocular drug delivery 267polymers ha
- Page 286 and 287:
Ocular drug delivery 269sustained-r
- Page 288 and 289:
Chapter TwelveVaginal and Intrauter
- Page 290 and 291:
Vaginal and intrauterine drug deliv
- Page 292 and 293:
Vaginal and intrauterine drug deliv
- Page 294 and 295:
Vaginal and intrauterine drug deliv
- Page 296 and 297:
Vaginal and intrauterine drug deliv
- Page 298:
Vaginal and intrauterine drug deliv
- Page 301 and 302:
284 GlossaryAntipyrine An analgesic
- Page 303 and 304:
286 GlossaryClonazepam An anticonvu
- Page 305 and 306:
288 GlossaryEsterase An enzyme whic
- Page 307 and 308:
290 Glossaryfound in the synovial f
- Page 309 and 310:
294 GlossaryPectoral muscle Chest m
- Page 311 and 312:
296 Glossarysize exclusion (gel fil
- Page 313 and 314:
298 GlossaryTributyrase An enzyme w
- Page 315 and 316:
300 Indexß-glucuronidase 276B cell
- Page 317 and 318:
302 IndexDiazoxide 262Dichlorodiphe
- Page 319 and 320:
304 IndexGelling polymers 264Gels 1
- Page 321 and 322:
306 IndexEpithelium 225Factors affe
- Page 323 and 324:
308 IndexOros ® 158Osmotic deliver
- Page 325 and 326:
310 IndexAbsorption 186Age 188Disea
- Page 327:
312 IndexDrug absorption 277Fluid 2