analysis of water injection into high-temperature mixture of ...
analysis of water injection into high-temperature mixture of ...
analysis of water injection into high-temperature mixture of ...
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
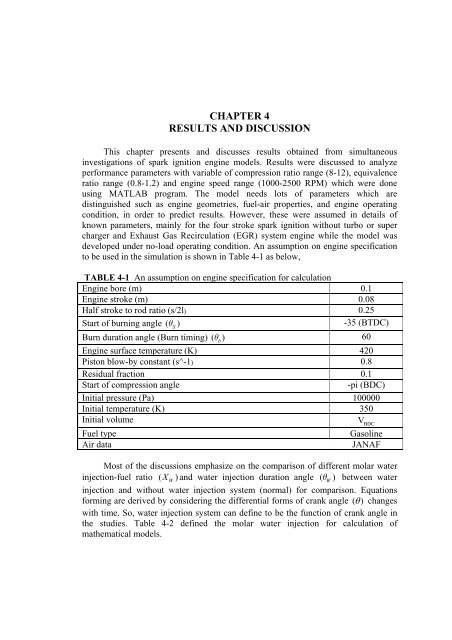
CHAPTER 4RESULTS AND DISCUSSIONThis chapter presents and discusses results obtained from simultaneousinvestigations <strong>of</strong> spark ignition engine models. Results were discussed to analyzeperformance parameters with variable <strong>of</strong> compression ratio range (8-12), equivalenceratio range (0.8-1.2) and engine speed range (1000-2500 RPM) which were doneusing MATLAB program. The model needs lots <strong>of</strong> parameters which aredistinguished such as engine geometries, fuel-air properties, and engine operatingcondition, in order to predict results. However, these were assumed in details <strong>of</strong>known parameters, mainly for the four stroke spark ignition without turbo or supercharger and Exhaust Gas Recirculation (EGR) system engine while the model wasdeveloped under no-load operating condition. An assumption on engine specificationto be used in the simulation is shown in Table 4-1 as below,TABLE 4-1 An assumption on engine specification for calculationEngine bore (m) 0.1Engine stroke (m) 0.08Half stroke to rod ratio (s/2l) 0.25Start <strong>of</strong> burning angle ( θ S)-35 (BTDC)Burn duration angle (Burn timing) (θb)60Engine surface <strong>temperature</strong> (K) 420Piston blow-by constant (s^-1) 0.8Residual fraction 0.1Start <strong>of</strong> compression angle-pi (BDC)Initial pressure (Pa) 100000Initial <strong>temperature</strong> (K) 350Initial volumeVBDCFuel typeGasolineAir dataJANAFMost <strong>of</strong> the discussions emphasize on the comparison <strong>of</strong> different molar <strong>water</strong><strong>injection</strong>-fuel ratio ( XW) and <strong>water</strong> <strong>injection</strong> duration angle ( θ W) between <strong>water</strong><strong>injection</strong> and without <strong>water</strong> <strong>injection</strong> system (normal) for comparison. Equationsforming are derived by considering the differential forms <strong>of</strong> crank angle ( θ ) changeswith time. So, <strong>water</strong> <strong>injection</strong> system can define to be the function <strong>of</strong> crank angle inthe studies. Table 4-2 defined the molar <strong>water</strong> <strong>injection</strong> for calculation <strong>of</strong>mathematical models.