1 - Acta Technica Corviniensis
1 - Acta Technica Corviniensis
1 - Acta Technica Corviniensis
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
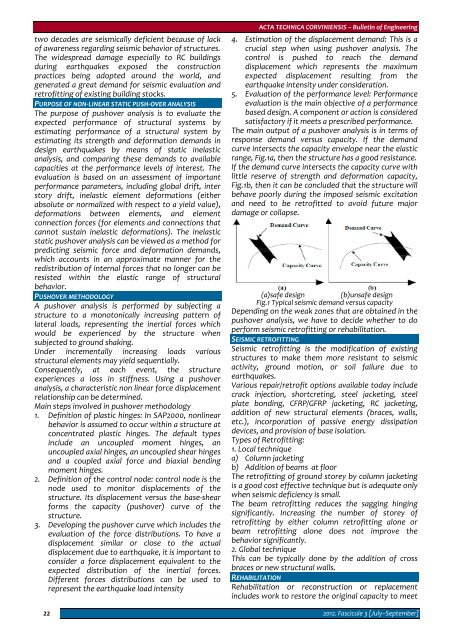
two decades are seismically deficient because of lackof awareness regarding seismic behavior of structures.The widespread damage especially to RC buildingsduring earthquakes exposed the constructionpractices being adopted around the world, andgenerated a great demand for seismic evaluation andretrofitting of existing building stocks.PURPOSE OF NON‐LINEAR STATIC PUSH‐OVER ANALYSISThe purpose of pushover analysis is to evaluate theexpected performance of structural systems byestimating performance of a structural system byestimating its strength and deformation demands indesign earthquakes by means of static inelasticanalysis, and comparing these demands to availablecapacities at the performance levels of interest. Theevaluation is based on an assessment of importantperformance parameters, including global drift, interstory drift, inelastic element deformations (eitherabsolute or normalized with respect to a yield value),deformations between elements, and elementconnection forces (for elements and connections thatcannot sustain inelastic deformations). The inelasticstatic pushover analysis can be viewed as a method forpredicting seismic force and deformation demands,which accounts in an approximate manner for theredistribution of internal forces that no longer can beresisted within the elastic range of structuralbehavior.PUSHOVER METHODOLOGYA pushover analysis is performed by subjecting astructure to a monotonically increasing pattern oflateral loads, representing the inertial forces whichwould be experienced by the structure whensubjected to ground shaking.Under incrementally increasing loads variousstructural elements may yield sequentially.Consequently, at each event, the structureexperiences a loss in stiffness. Using a pushoveranalysis, a characteristic non linear force displacementrelationship can be determined.Main steps involved in pushover methodology1. Definition of plastic hinges: In SAP2000, nonlinearbehavior is assumed to occur within a structure atconcentrated plastic hinges. The default typesinclude an uncoupled moment hinges, anuncoupled axial hinges, an uncoupled shear hingesand a coupled axial force and biaxial bendingmoment hinges.2. Definition of the control node: control node is thenode used to monitor displacements of thestructure. Its displacement versus the base‐shearforms the capacity (pushover) curve of thestructure.3. Developing the pushover curve which includes theevaluation of the force distributions. To have adisplacement similar or close to the actualdisplacement due to earthquake, it is important toconsider a force displacement equivalent to theexpected distribution of the inertial forces.Different forces distributions can be used torepresent the earthquake load intensity22ACTA TECHNICA CORVINIENSIS – Bulletin of Engineering4. Estimation of the displacement demand: This is acrucial step when using pushover analysis. Thecontrol is pushed to reach the demanddisplacement which represents the maximumexpected displacement resulting from theearthquake intensity under consideration.5. Evaluation of the performance level: Performanceevaluation is the main objective of a performancebased design. A component or action is consideredsatisfactory if it meets a prescribed performance.The main output of a pushover analysis is in terms ofresponse demand versus capacity. If the demandcurve intersects the capacity envelope near the elasticrange, Fig.1a, then the structure has a good resistance.If the demand curve intersects the capacity curve withlittle reserve of strength and deformation capacity,Fig.1b, then it can be concluded that the structure willbehave poorly during the imposed seismic excitationand need to be retrofitted to avoid future majordamage or collapse.(a)safe design (b)unsafe designFig.1 Typical seismic demand versus capacityDepending on the weak zones that are obtained in thepushover analysis, we have to decide whether to doperform seismic retrofitting or rehabilitation.SEISMIC RETROFITTINGSeismic retrofitting is the modification of existingstructures to make them more resistant to seismicactivity, ground motion, or soil failure due toearthquakes.Various repair/retrofit options available today includecrack injection, shortcreting, steel jacketing, steelplate bonding, CFRP/GFRP jacketing, RC jacketing,addition of new structural elements (braces, walls,etc.), incorporation of passive energy dissipationdevices, and provision of base isolation.Types of Retrofitting:1. Local techniquea) Column jacketingb) Addition of beams at floorThe retrofitting of ground storey by column jacketingis a good cost effective technique but is adequate onlywhen seismic deficiency is small.The beam retrofitting reduces the sagging hingingsignificantly. Increasing the number of storey ofretrofitting by either column retrofitting alone orbeam retrofitting alone does not improve thebehavior significantly.2. Global techniqueThis can be typically done by the addition of crossbraces or new structural walls.REHABILITATIONRehabilitation or reconstruction or replacementincludes work to restore the original capacity to meet2012. Fascicule 3 [July–September]