- Page 1 and 2:
CopyrightbyDavid Andrew Dunkman2009
- Page 3 and 4:
Bursting and Spalling in Pretension
- Page 5 and 6:
Bursting and Spalling in Pretension
- Page 7 and 8:
2.4.2.3 Itani & Galbraith, 1986 ...
- Page 9 and 10:
4.2.2.4 Beam 1: Lateral-Bar Burstin
- Page 11 and 12:
List of TablesTable 2.1 Range of st
- Page 13 and 14:
Figure 2.25 Mechanical gage points
- Page 15 and 16:
Figure 3.30 Thermocouple placement
- Page 17:
CHAPTER 1Introduction1.1 IMPETUS FO
- Page 20:
At present, current end-region deta
- Page 23 and 24:
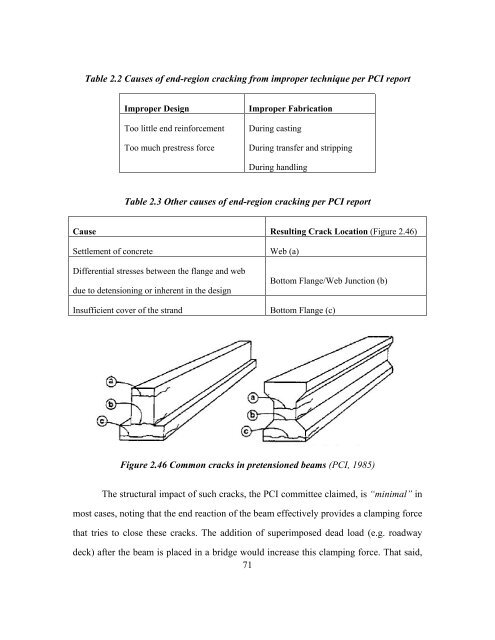
Figure 2.1 Severe cracking in a pre
- Page 25 and 26:
through use of tensioned, high-stre
- Page 27 and 28:
As splitting stress is bond-related
- Page 29 and 30:
Figure 2.6 Effect of bursting & spa
- Page 31 and 32:
magnitude of the end-region transve
- Page 33 and 34:
FEA can readily output color maps o
- Page 35 and 36: 2.3.1.3 Plastic Analysis of Beam En
- Page 38 and 39: force can increase by 400% (Yettram
- Page 40 and 41: 2.4 EXPERIMENTAL STUDIES OF BURSTIN
- Page 42 and 43: The trial specimens included one 40
- Page 44 and 45: mechanical gage (2 in. gage length)
- Page 46 and 47: Bursting stress(normalized by prest
- Page 48 and 49: proprietary post-tensioning anchors
- Page 50 and 51: Though Marshall and Mattock placed
- Page 52 and 53: ectangular beam” (p. 21). At high
- Page 54 and 55: Most beams observed to crack did so
- Page 56 and 57: The behavior of these beams was dom
- Page 58 and 59: 2.4.2 Studies of End-Region Transve
- Page 60 and 61: Figure 2.28 I-beams studied by Mars
- Page 62 and 63: transverse forces compared to those
- Page 64 and 65: (a) Actual spalling stress variatio
- Page 66 and 67: stirrups in Gergely, Sozen and Sies
- Page 68 and 69: 50% more reinforcement than require
- Page 70 and 71: strength concrete, increasingly hig
- Page 72 and 73: the reinforcement located within th
- Page 74 and 75: Typical crack patterns for the beam
- Page 76 and 77: “Very common”crack locationPred
- Page 78 and 79: Figure 2.38 Typical gage locations
- Page 80 and 81: 2.4.2.7 Smith et al., 2008Most rece
- Page 82 and 83: the provided transverse reinforceme
- Page 84 and 85: Itani and Galbraith (1986) reported
- Page 88 and 89: cracks located along lines of prest
- Page 90 and 91: odies relevant to pretensioned conc
- Page 92 and 93: than that in another shape. For thi
- Page 94 and 95: Figure 2.47 Required splitting rein
- Page 96 and 97: No attempt was made in the Tentativ
- Page 98 and 99: No citation is provided in the PCI
- Page 100 and 101: Section Propertiesy b22.4 in.A 1120
- Page 102 and 103: minimum for greater skews. For beam
- Page 104 and 105: treatment (counting the transverse
- Page 106 and 107: Pretensioned/post-tensioned beams h
- Page 108 and 109: Figure 2.57 Harped strands in webs
- Page 110 and 111: transversereinforcementwithin voidp
- Page 112 and 113: 2.8 SUMMARYIn this chapter, literat
- Page 114 and 115: 3.2.1.1 Linear and Nonlinear Stress
- Page 116 and 117: Empirical expressions can be used t
- Page 118 and 119: where: 0.021 = spalling force,
- Page 120 and 121: 3.3 CONCRETE PROPERTIES3.3.1 Concre
- Page 122 and 123: It was reasoned that the dimensiona
- Page 124 and 125: Splitting tensile-strength testing
- Page 126 and 127: For temperature-match curing, therm
- Page 128 and 129: 3.4.1 Reinforcing-Bar Mechanical Te
- Page 130 and 131: Grade 60 rebar yielded at 65 ksi an
- Page 132 and 133: Equation 3.10where:ε1,2 = gage str
- Page 134 and 135: Figure 3.17 Typical strand failure
- Page 136 and 137:
SouthNorth North120NorthSouthFigure
- Page 138 and 139:
Beam 1 also included an additional
- Page 140 and 141:
Figure 3.22 Strand strain-gage inst
- Page 142 and 143:
Figure 3.25 Interface board used to
- Page 144 and 145:
eam has a “hot spot” (measureme
- Page 146 and 147:
3.6 BEAM FABRICATION3.6.1 Beam Cast
- Page 148 and 149:
Figure 3.33 Installing the interior
- Page 150 and 151:
In order to use a pretensioning bed
- Page 152 and 153:
standardside-formprofilespecialtape
- Page 154 and 155:
Figure 3.41 Strands installed, tens
- Page 156 and 157:
Correspondence between the values o
- Page 158 and 159:
Figures 3.45 to 3.50 show the fabri
- Page 160 and 161:
Figure 3.49 Casting end block (and
- Page 162 and 163:
Figure 3.52 Detensioning by gradual
- Page 164 and 165:
CHAPTER 4Results & Discussion4.1 OV
- Page 166 and 167:
The strain time history for each ga
- Page 168 and 169:
1DNorthSouth1E18 ksi1C1C,E1D1521B1B
- Page 170 and 171:
Figure 4.4 Beam 1 prestress losses
- Page 172 and 173:
crack adjacent to this location was
- Page 174 and 175:
The temperatures in the end blocks
- Page 176 and 177:
Table 4.4 Beam 2 applied prestressi
- Page 178 and 179:
Figure 4.10 Beam 2 prestress losses
- Page 180 and 181:
terms of force distribution seems t
- Page 182 and 183:
limits were only exceeded at locati
- Page 184 and 185:
spalling stresses were measured in
- Page 186 and 187:
transverse reinforcement contained
- Page 188 and 189:
Based on Figure 4.18, the 4% Pi des
- Page 190 and 191:
Uniform and linearly-decreasing tra
- Page 192 and 193:
4.3.5 Contributing Factors to High
- Page 194 and 195:
stress ratio multiplied by a typica
- Page 196 and 197:
Figure 4.25 Relation between total
- Page 198 and 199:
4.4.1 Recommended Texas U-Beam Rein
- Page 200 and 201:
Figure 4.28 Proposed end-region det
- Page 202 and 203:
At present, AASHTO LRFD (2009) lack
- Page 204 and 205:
CHAPTER 5Conclusions5.1 SUMMARY OF
- Page 206 and 207:
tested at transfer and under shear
- Page 208 and 209:
APPENDIX ADatabase of Transverse-Ba
- Page 210 and 211:
194Figure A.1 U-beam with skewed en
- Page 212 and 213:
196Figure A.3 Shallow Texas bulb te
- Page 214 and 215:
198Figure A.5 Lightweight-concrete
- Page 216 and 217:
200Figure A.7 Washington bulb tee (
- Page 218 and 219:
202Figure A.9 Nebraska bulb tees an
- Page 220 and 221:
204Figure A.11 Nebraska bulb tees a
- Page 222 and 223:
206Figure A.13 Shallow I-beams
- Page 224 and 225:
where:= lower-bound concrete tensil
- Page 226 and 227:
B.3.4 Transmission Length (Clause 6
- Page 228 and 229:
Equation B.11where:= bursting force
- Page 230 and 231:
50High Web gage4030Max Moment heigh
- Page 232 and 233:
C.2 CONCRETE RELEASE STRENGTHA bott
- Page 234 and 235:
Table C.1 Specimen Design for Beams
- Page 236 and 237:
Table D.1 Beam 1 match-cured cylind
- Page 238 and 239:
D.1.2 Beam 28Release-Point Cylinder
- Page 240 and 241:
Cylinder Strength (ksi)131197Ambien
- Page 242 and 243:
D.2 REINFORCING-BAR MODULUS & STREN
- Page 244 and 245:
APPENDIX EEnd-Block Temperature Pro
- Page 246 and 247:
E.2 BEAM 2T max = 142°F∆T = 30°
- Page 248 and 249:
REFERENCESREFERENCED STANDARDSAmeri
- Page 250 and 251:
Fédération Internationale du Bét
- Page 252 and 253:
Davis, R.T.; Buckner, C.D. & Ozyild
- Page 254 and 255:
Lin, T.Y. & Burns, N.H. (1981), Des
- Page 256 and 257:
Stone, W.C. & Breen, J.E. (1984),
- Page 258:
VITADavid Andrew Dunkman was born 2