DBI Analysis of Open String Bound States on Non-compact D-branes
DBI Analysis of Open String Bound States on Non-compact D-branes
DBI Analysis of Open String Bound States on Non-compact D-branes
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
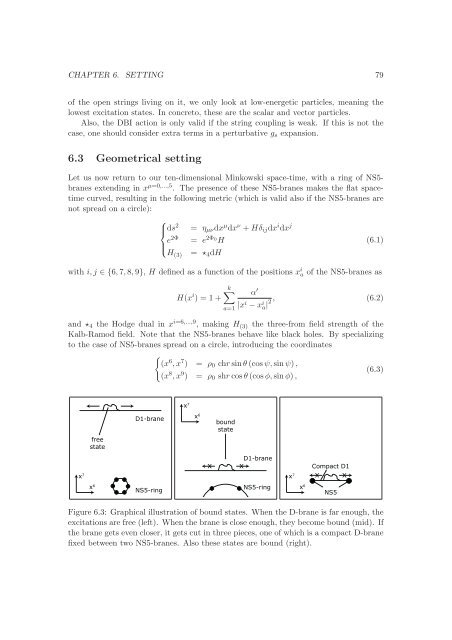
CHAPTER 6. SETTING 79<str<strong>on</strong>g>of</str<strong>on</strong>g> the open strings living <strong>on</strong> it, we <strong>on</strong>ly look at low-energetic particles, meaning thelowest excitati<strong>on</strong> states. In c<strong>on</strong>creto, these are the scalar and vector particles.Also, the <str<strong>on</strong>g>DBI</str<strong>on</strong>g> acti<strong>on</strong> is <strong>on</strong>ly valid if the string coupling is weak. If this is not thecase, <strong>on</strong>e should c<strong>on</strong>sider extra terms in a perturbative g s expansi<strong>on</strong>.6.3 Geometrical settingLet us now return to our ten-dimensi<strong>on</strong>al Minkowski space-time, with a ring <str<strong>on</strong>g>of</str<strong>on</strong>g> NS5-<strong>branes</strong> extending in x µ=0,...,5 . The presence <str<strong>on</strong>g>of</str<strong>on</strong>g> these NS5-<strong>branes</strong> makes the flat spacetimecurved, resulting in the following metric (which is valid also if the NS5-<strong>branes</strong> arenot spread <strong>on</strong> a circle):⎧⎪⎨ ds 2 = η µν dx µ dx ν + Hδ ij dx i dx je⎪⎩2Φ = e 2Φ 0H(6.1)= ⋆ 4 dHH (3)with i, j ∈ {6, 7, 8, 9}, H defined as a functi<strong>on</strong> <str<strong>on</strong>g>of</str<strong>on</strong>g> the positi<strong>on</strong>s x i a <str<strong>on</strong>g>of</str<strong>on</strong>g> the NS5-<strong>branes</strong> asH(x i ) = 1 +k∑ α ′|x i − x i 2, (6.2)a|a=1and ⋆ 4 the Hodge dual in x i=6,...,9 , making H (3) the three-from field strength <str<strong>on</strong>g>of</str<strong>on</strong>g> theKalb-Ramod field. Note that the NS5-<strong>branes</strong> behave like black holes. By specializingto the case <str<strong>on</strong>g>of</str<strong>on</strong>g> NS5-<strong>branes</strong> spread <strong>on</strong> a circle, introducing the coordinates{(x 6 , x 7 ) = ρ 0 chr sinθ (cos ψ, sinψ),(x 8 , x 9 (6.3)) = ρ 0 shr cos θ (cos φ,sinφ) ,D1-branex 6x 7 x xboundstatefreestatex 7D1-braneCompact D1x 7 x xx 6NS5-ringNS5-ringx 6NS5Figure 6.3: Graphical illustrati<strong>on</strong> <str<strong>on</strong>g>of</str<strong>on</strong>g> bound states. When the D-brane is far enough, theexcitati<strong>on</strong>s are free (left). When the brane is close enough, they become bound (mid). Ifthe brane gets even closer, it gets cut in three pieces, <strong>on</strong>e <str<strong>on</strong>g>of</str<strong>on</strong>g> which is a <strong>compact</strong> D-branefixed between two NS5-<strong>branes</strong>. Also these states are bound (right).