Strategic Guidance on the Management of LLW and ILW / LLW ...
Strategic Guidance on the Management of LLW and ILW / LLW ...
Strategic Guidance on the Management of LLW and ILW / LLW ...
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
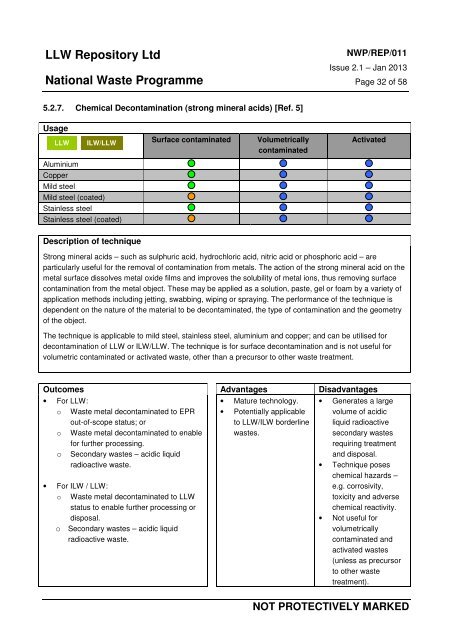
<strong>LLW</strong> Repository LtdNati<strong>on</strong>al Waste ProgrammeNWP/REP/011Issue 2.1 – Jan 2013Page 32 <strong>of</strong> 585.2.7. Chemical Dec<strong>on</strong>taminati<strong>on</strong> (str<strong>on</strong>g mineral acids) [Ref. 5]Usage<strong>LLW</strong><strong>ILW</strong>/<strong>LLW</strong>Surface c<strong>on</strong>taminatedVolumetricallyc<strong>on</strong>taminatedActivatedAluminiumCopperMild steelMild steel (coated)Stainless steelStainless steel (coated)Descripti<strong>on</strong> <strong>of</strong> techniqueStr<strong>on</strong>g mineral acids – such as sulphuric acid, hydrochloric acid, nitric acid or phosphoric acid – areparticularly useful for <strong>the</strong> removal <strong>of</strong> c<strong>on</strong>taminati<strong>on</strong> from metals. The acti<strong>on</strong> <strong>of</strong> <strong>the</strong> str<strong>on</strong>g mineral acid <strong>on</strong> <strong>the</strong>metal surface dissolves metal oxide films <strong>and</strong> improves <strong>the</strong> solubility <strong>of</strong> metal i<strong>on</strong>s, thus removing surfacec<strong>on</strong>taminati<strong>on</strong> from <strong>the</strong> metal object. These may be applied as a soluti<strong>on</strong>, paste, gel or foam by a variety <strong>of</strong>applicati<strong>on</strong> methods including jetting, swabbing, wiping or spraying. The performance <strong>of</strong> <strong>the</strong> technique isdependent <strong>on</strong> <strong>the</strong> nature <strong>of</strong> <strong>the</strong> material to be dec<strong>on</strong>taminated, <strong>the</strong> type <strong>of</strong> c<strong>on</strong>taminati<strong>on</strong> <strong>and</strong> <strong>the</strong> geometry<strong>of</strong> <strong>the</strong> object.The technique is applicable to mild steel, stainless steel, aluminium <strong>and</strong> copper; <strong>and</strong> can be utilised fordec<strong>on</strong>taminati<strong>on</strong> <strong>of</strong> <strong>LLW</strong> or <strong>ILW</strong>/<strong>LLW</strong>. The technique is for surface dec<strong>on</strong>taminati<strong>on</strong> <strong>and</strong> is not useful forvolumetric c<strong>on</strong>taminated or activated waste, o<strong>the</strong>r than a precursor to o<strong>the</strong>r waste treatment.Outcomes Advantages Disadvantages• For <strong>LLW</strong>:o Waste metal dec<strong>on</strong>taminated to EPRout-<strong>of</strong>-scope status; oro Waste metal dec<strong>on</strong>taminated to enablefor fur<strong>the</strong>r processing.o Sec<strong>on</strong>dary wastes – acidic liquidradioactive waste.• For <strong>ILW</strong> / <strong>LLW</strong>:o Waste metal dec<strong>on</strong>taminated to <strong>LLW</strong>status to enable fur<strong>the</strong>r processing ordisposal.o Sec<strong>on</strong>dary wastes – acidic liquidradioactive waste.A company owned by UK Nuclear Waste <strong>Management</strong> Ltd• Mature technology.• Potentially applicableto <strong>LLW</strong>/<strong>ILW</strong> borderlinewastes.• Generates a largevolume <strong>of</strong> acidicliquid radioactivesec<strong>on</strong>dary wastesrequiring treatment<strong>and</strong> disposal.• Technique poseschemical hazards –e.g. corrosivity,toxicity <strong>and</strong> adversechemical reactivity.• Not useful forvolumetricallyc<strong>on</strong>taminated <strong>and</strong>activated wastes(unless as precursorto o<strong>the</strong>r wastetreatment).NOT PROTECTIVELY MARKED