Interventions to build resilience among young people A literature review
Interventions-to-build-resilience-among-young-people
Interventions-to-build-resilience-among-young-people
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
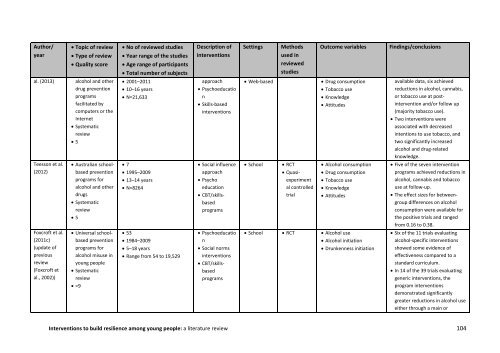
Author/<br />
year<br />
Topic of <strong>review</strong><br />
Type of <strong>review</strong><br />
Quality score<br />
No of <strong>review</strong>ed studies<br />
Year range of the studies<br />
Age range of participants<br />
Total number of subjects<br />
Description of<br />
interventions<br />
Settings<br />
Methods<br />
used in<br />
<strong>review</strong>ed<br />
studies<br />
Outcome variables<br />
Findings/conclusions<br />
al. (2013)<br />
alcohol and other<br />
drug prevention<br />
programs<br />
facilitated by<br />
computers or the<br />
Internet<br />
Systematic<br />
<strong>review</strong><br />
5<br />
2001–2011<br />
10–16 years<br />
N=21,633<br />
approach<br />
Psychoeducatio<br />
n<br />
Skills-based<br />
interventions<br />
Web-based<br />
Drug consumption<br />
Tobacco use<br />
Knowledge<br />
Attitudes<br />
available data, six achieved<br />
reductions in alcohol, cannabis,<br />
or <strong>to</strong>bacco use at postintervention<br />
and/or follow up<br />
(majority <strong>to</strong>bacco use).<br />
Two interventions were<br />
associated with decreased<br />
intentions <strong>to</strong> use <strong>to</strong>bacco, and<br />
two significantly increased<br />
alcohol and drug-related<br />
knowledge.<br />
Teesson et al.<br />
(2012)<br />
Australian schoolbased<br />
prevention<br />
programs for<br />
alcohol and other<br />
drugs<br />
Systematic<br />
<strong>review</strong><br />
5<br />
7<br />
1995–2009<br />
13–14 years<br />
N=8264<br />
Social influence<br />
approach<br />
Psycho<br />
education<br />
CBT/skillsbased<br />
programs<br />
School<br />
RCT<br />
Quasiexperiment<br />
al controlled<br />
trial<br />
Alcohol consumption<br />
Drug consumption<br />
Tobacco use<br />
Knowledge<br />
Attitudes<br />
Five of the seven intervention<br />
programs achieved reductions in<br />
alcohol, cannabis and <strong>to</strong>bacco<br />
use at follow-up.<br />
The effect sizes for betweengroup<br />
differences on alcohol<br />
consumption were available for<br />
the positive trials and ranged<br />
from 0.16 <strong>to</strong> 0.38.<br />
Foxcroft et al.<br />
(2011c)<br />
(update of<br />
previous<br />
<strong>review</strong><br />
(Foxcroft et<br />
al., 2002))<br />
Universal schoolbased<br />
prevention<br />
programs for<br />
alcohol misuse in<br />
<strong>young</strong> <strong>people</strong><br />
Systematic<br />
<strong>review</strong><br />
=9<br />
53<br />
1984–2009<br />
5–18 years<br />
Range from 54 <strong>to</strong> 19,529<br />
Psychoeducatio<br />
n<br />
Social norms<br />
interventions<br />
CBT/skillsbased<br />
programs<br />
School RCT Alcohol use<br />
Alcohol initiation<br />
Drunkenness initiation<br />
Six of the 11 trials evaluating<br />
alcohol-specific interventions<br />
showed some evidence of<br />
effectiveness compared <strong>to</strong> a<br />
standard curriculum.<br />
In 14 of the 39 trials evaluating<br />
generic interventions, the<br />
program interventions<br />
demonstrated significantly<br />
greater reductions in alcohol use<br />
either through a main or<br />
<strong>Interventions</strong> <strong>to</strong> <strong>build</strong> <strong>resilience</strong> <strong>among</strong> <strong>young</strong> <strong>people</strong>: a <strong>literature</strong> <strong>review</strong> 104