Interventions to build resilience among young people A literature review
Interventions-to-build-resilience-among-young-people
Interventions-to-build-resilience-among-young-people
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
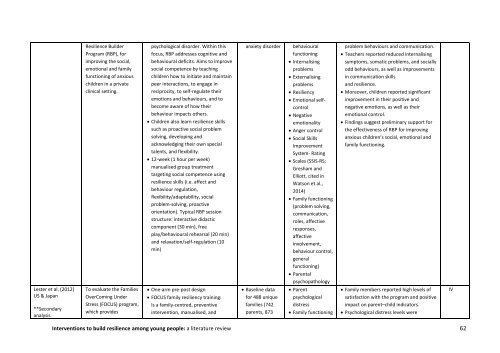
Resilience Builder<br />
Program (RBP), for<br />
improving the social,<br />
emotional and family<br />
functioning of anxious<br />
children in a private<br />
clinical setting.<br />
psychological disorder. Within this<br />
focus, RBP addresses cognitive and<br />
behavioural deficits. Aims <strong>to</strong> improve<br />
social competence by teaching<br />
children how <strong>to</strong> initiate and maintain<br />
peer interactions, <strong>to</strong> engage in<br />
reciprocity, <strong>to</strong> self-regulate their<br />
emotions and behaviours, and <strong>to</strong><br />
become aware of how their<br />
behaviour impacts others.<br />
Children also learn <strong>resilience</strong> skills<br />
such as proactive social problem<br />
solving, developing and<br />
acknowledging their own special<br />
talents, and flexibility.<br />
12-week (1 hour per week)<br />
manualised group treatment<br />
targeting social competence using<br />
<strong>resilience</strong> skills (i.e. affect and<br />
behaviour regulation,<br />
flexibility/adaptability, social<br />
problem-solving, proactive<br />
orientation). Typical RBP session<br />
structure: interactive didactic<br />
component (30 min), free<br />
play/behavioural rehearsal (20 min)<br />
and relaxation/self-regulation (10<br />
min)<br />
anxiety disorder<br />
behavioural<br />
functioning<br />
Internalising<br />
problems<br />
Externalising<br />
problems<br />
Resiliency<br />
Emotional selfcontrol<br />
Negative<br />
emotionality<br />
Anger control<br />
Social Skills<br />
Improvement<br />
System- Rating<br />
Scales (SSIS-RS;<br />
Gresham and<br />
Elliott, cited in<br />
Watson et al.,<br />
2014)<br />
Family functioning<br />
(problem solving,<br />
communication,<br />
roles, affective<br />
responses,<br />
affective<br />
involvement,<br />
behaviour control,<br />
general<br />
functioning)<br />
problem behaviours and communication.<br />
Teachers reported reduced internalising<br />
symp<strong>to</strong>ms, somatic problems, and socially<br />
odd behaviours, as well as improvements<br />
in communication skills<br />
and <strong>resilience</strong>.<br />
Moreover, children reported significant<br />
improvement in their positive and<br />
negative emotions, as well as their<br />
emotional control.<br />
Findings suggest preliminary support for<br />
the effectiveness of RBP for improving<br />
anxious children’s social, emotional and<br />
family functioning.<br />
Parental<br />
psychopathology<br />
Lester et al. (2012)<br />
US & Japan<br />
**Secondary<br />
analysis<br />
To evaluate the Families<br />
OverComing Under<br />
Stress (FOCUS) program,<br />
which provides<br />
One-arm pre-post design<br />
FOCUS family resiliency training:<br />
Is a family-centred, preventive<br />
intervention, manualised, and<br />
Baseline data<br />
for 488 unique<br />
families (742<br />
parents, 873<br />
Parent<br />
psychological<br />
distress<br />
Family functioning<br />
Family members reported high levels of<br />
satisfaction with the program and positive<br />
impact on parent–child indica<strong>to</strong>rs.<br />
Psychological distress levels were<br />
IV<br />
<strong>Interventions</strong> <strong>to</strong> <strong>build</strong> <strong>resilience</strong> <strong>among</strong> <strong>young</strong> <strong>people</strong>: a <strong>literature</strong> <strong>review</strong> 62