Interventions to build resilience among young people A literature review
Interventions-to-build-resilience-among-young-people
Interventions-to-build-resilience-among-young-people
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
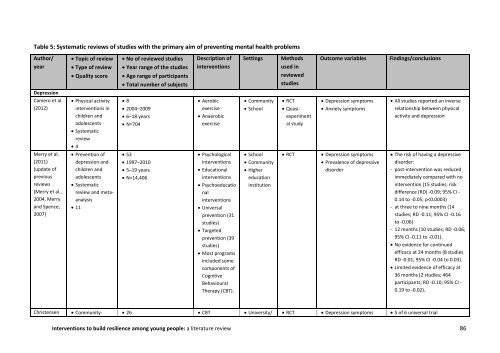
Table 5: Systematic <strong>review</strong>s of studies with the primary aim of preventing mental health problems<br />
Author/<br />
year<br />
Topic of <strong>review</strong><br />
Type of <strong>review</strong><br />
Quality score<br />
No of <strong>review</strong>ed studies<br />
Year range of the studies<br />
Age range of participants<br />
Total number of subjects<br />
Description of<br />
interventions<br />
Settings<br />
Methods<br />
used in<br />
<strong>review</strong>ed<br />
studies<br />
Outcome variables<br />
Findings/conclusions<br />
Depression<br />
Camero et al.<br />
(2012)<br />
Physical activity<br />
interventions in<br />
children and<br />
adolescents<br />
Systematic<br />
<strong>review</strong><br />
4<br />
8<br />
2004–2009<br />
6–18 years<br />
N=704<br />
Aerobic<br />
exercise<br />
Anaerobic<br />
exercise<br />
Community<br />
School<br />
RCT<br />
Quasiexperiment<br />
al study<br />
Depression symp<strong>to</strong>ms<br />
Anxiety symp<strong>to</strong>ms<br />
All studies reported an inverse<br />
relationship between physical<br />
activity and depression<br />
Merry et al.<br />
(2011)<br />
(update of<br />
previous<br />
<strong>review</strong>s<br />
(Merry et al.,<br />
2004, Merry<br />
and Spence,<br />
2007)<br />
Prevention of<br />
depression and<br />
children and<br />
adolescents<br />
Systematic<br />
<strong>review</strong> and metaanalysis<br />
11<br />
53<br />
1997–2010<br />
5–19 years<br />
N=14,406<br />
Psychological<br />
interventions<br />
Educational<br />
interventions<br />
Psychoeducatio<br />
nal<br />
interventions<br />
Universal<br />
prevention (31<br />
studies)<br />
Targeted<br />
prevention (39<br />
studies)<br />
Most programs<br />
included some<br />
components of<br />
Cognitive<br />
Behavioural<br />
Therapy (CBT).<br />
School<br />
Community<br />
Higher<br />
education<br />
institution<br />
RCT<br />
Depression symp<strong>to</strong>ms<br />
Prevalence of depressive<br />
disorder<br />
The risk of having a depressive<br />
disorder:<br />
- post-intervention was reduced<br />
immediately compared with no<br />
intervention (15 studies; risk<br />
difference (RD) -0.09; 95% CI -<br />
0.14 <strong>to</strong> -0.05; p