Interventions to build resilience among young people A literature review
Interventions-to-build-resilience-among-young-people
Interventions-to-build-resilience-among-young-people
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
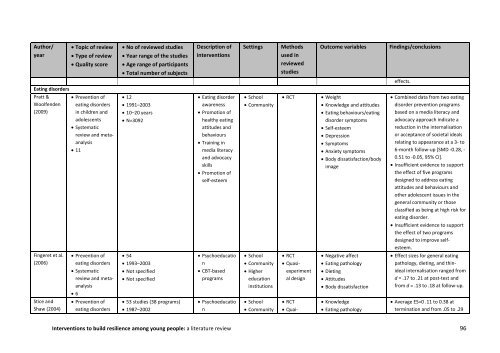
Author/<br />
year<br />
Topic of <strong>review</strong><br />
Type of <strong>review</strong><br />
Quality score<br />
No of <strong>review</strong>ed studies<br />
Year range of the studies<br />
Age range of participants<br />
Total number of subjects<br />
Description of<br />
interventions<br />
Settings<br />
Methods<br />
used in<br />
<strong>review</strong>ed<br />
studies<br />
Outcome variables<br />
Findings/conclusions<br />
effects.<br />
Eating disorders<br />
Pratt &<br />
Woolfenden<br />
(2009)<br />
Prevention of<br />
eating disorders<br />
in children and<br />
adolescents<br />
Systematic<br />
<strong>review</strong> and metaanalysis<br />
11<br />
12<br />
1991–2003<br />
10–20 years<br />
N=3092<br />
Eating disorder<br />
awareness<br />
Promotion of<br />
healthy eating<br />
attitudes and<br />
behaviours<br />
Training in<br />
media literacy<br />
and advocacy<br />
skills<br />
Promotion of<br />
self-esteem<br />
School<br />
Community<br />
RCT<br />
Weight<br />
Knowledge and attitudes<br />
Eating behaviours/eating<br />
disorder symp<strong>to</strong>ms<br />
Self-esteem<br />
Depression<br />
Symp<strong>to</strong>ms<br />
Anxiety symp<strong>to</strong>ms<br />
Body dissatisfaction/body<br />
image<br />
Combined data from two eating<br />
disorder prevention programs<br />
based on a media literacy and<br />
advocacy approach indicate a<br />
reduction in the internalisation<br />
or acceptance of societal ideals<br />
relating <strong>to</strong> appearance at a 3- <strong>to</strong><br />
6-month follow-up [SMD -0.28, -<br />
0.51 <strong>to</strong> -0.05, 95% CI].<br />
Insufficient evidence <strong>to</strong> support<br />
the effect of five programs<br />
designed <strong>to</strong> address eating<br />
attitudes and behaviours and<br />
other adolescent issues in the<br />
general community or those<br />
classified as being at high risk for<br />
eating disorder.<br />
Insufficient evidence <strong>to</strong> support<br />
the effect of two programs<br />
designed <strong>to</strong> improve selfesteem.<br />
Fingeret et al.<br />
(2006)<br />
Prevention of<br />
eating disorders<br />
Systematic<br />
<strong>review</strong> and metaanalysis<br />
6<br />
54<br />
1993–2003<br />
Not specified<br />
Not specified<br />
Psychoeducatio<br />
n<br />
CBT-based<br />
programs<br />
School<br />
Community<br />
Higher<br />
education<br />
institutions<br />
RCT<br />
Quasiexperiment<br />
al design<br />
Negative affect<br />
Eating pathology<br />
Dieting<br />
Attitudes<br />
Body dissatisfaction<br />
Effect sizes for general eating<br />
pathology, dieting, and thinideal<br />
internalisation ranged from<br />
d = .17 <strong>to</strong> .21 at post-test and<br />
from d = .13 <strong>to</strong> .18 at follow-up.<br />
Stice and<br />
Shaw (2004)<br />
Prevention of<br />
eating disorders<br />
53 studies (38 programs)<br />
1987–2002<br />
Psychoeducatio<br />
n<br />
School<br />
Community<br />
RCT<br />
Quai-<br />
Knowledge<br />
Eating pathology<br />
Average ES=0 .11 <strong>to</strong> 0.38 at<br />
termination and from .05 <strong>to</strong> .29<br />
<strong>Interventions</strong> <strong>to</strong> <strong>build</strong> <strong>resilience</strong> <strong>among</strong> <strong>young</strong> <strong>people</strong>: a <strong>literature</strong> <strong>review</strong> 96