Semantics
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
BASIC CONCEPTS II 45<br />
These ideas include the link between knowledge and language, the<br />
definition of language, what kind of knowledge is linguistic knowledge,<br />
the basic aspects of language acquisition, the relationship between language<br />
description and philosophy and, finally those kinds of methods of analysis<br />
which are mainly used in linguistics.<br />
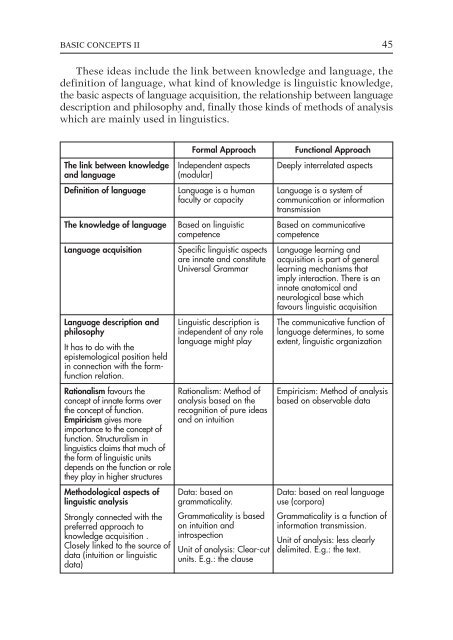
The link between knowledge<br />
and language<br />
Definition of language<br />
The knowledge of language<br />
Language acquisition<br />
Language description and<br />
philosophy<br />
It has to do with the<br />
epistemological position held<br />
in connection with the formfunction<br />
relation.<br />
Rationalism favours the<br />
concept of innate forms over<br />
the concept of function.<br />
Empiricism gives more<br />
importance to the concept of<br />
function. Structuralism in<br />
linguistics claims that much of<br />
the form of linguistic units<br />
depends on the function or role<br />
they play in higher structures<br />
Methodological aspects of<br />
linguistic analysis<br />
Strongly connected with the<br />
preferred approach to<br />
knowledge acquisition .<br />
Closely linked to the source of<br />
data (intuition or linguistic<br />
data)<br />
Formal Approach<br />
Independent aspects<br />
(modular)<br />
Language is a human<br />
faculty or capacity<br />
Based on linguistic<br />
competence<br />
Specific linguistic aspects<br />
are innate and constitute<br />
Universal Grammar<br />
Linguistic description is<br />
independent of any role<br />
language might play<br />
Rationalism: Method of<br />
analysis based on the<br />
recognition of pure ideas<br />
and on intuition<br />
Data: based on<br />
grammaticality.<br />
Grammaticality is based<br />
on intuition and<br />
introspection<br />
Unit of analysis: Clear-cut<br />
units. E.g.: the clause<br />
Functional Approach<br />
Deeply interrelated aspects<br />
Language is a system of<br />
communication or information<br />
transmission<br />
Based on communicative<br />
competence<br />
Language learning and<br />
acquisition is part of general<br />
learning mechanisms that<br />
imply interaction. There is an<br />
innate anatomical and<br />
neurological base which<br />
favours linguistic acquisition<br />
The communicative function of<br />
language determines, to some<br />
extent, linguistic organization<br />
Empiricism: Method of analysis<br />
based on observable data<br />
Data: based on real language<br />
use (corpora)<br />
Grammaticality is a function of<br />
information transmission.<br />
Unit of analysis: less clearly<br />
delimited. E.g.: the text.