BATTLEFIELD DIGITAL FORENSICS
BDF_Battlefield_Digital_Forensics_final
BDF_Battlefield_Digital_Forensics_final
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
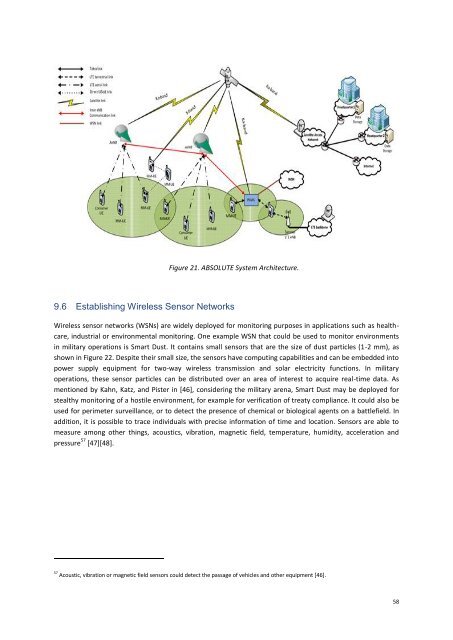
Figure 21. ABSOLUTE System Architecture.<br />
9.6 Establishing Wireless Sensor Networks<br />
Wireless sensor networks (WSNs) are widely deployed for monitoring purposes in applications such as healthcare,<br />
industrial or environmental monitoring. One example WSN that could be used to monitor environments<br />
in military operations is Smart Dust. It contains small sensors that are the size of dust particles (1-2 mm), as<br />
shown in Figure 22. Despite their small size, the sensors have computing capabilities and can be embedded into<br />
power supply equipment for two-way wireless transmission and solar electricity functions. In military<br />
operations, these sensor particles can be distributed over an area of interest to acquire real-time data. As<br />
mentioned by Kahn, Katz, and Pister in [46], considering the military arena, Smart Dust may be deployed for<br />
stealthy monitoring of a hostile environment, for example for verification of treaty compliance. It could also be<br />
used for perimeter surveillance, or to detect the presence of chemical or biological agents on a battlefield. In<br />
addition, it is possible to trace individuals with precise information of time and location. Sensors are able to<br />
measure among other things, acoustics, vibration, magnetic field, temperature, humidity, acceleration and<br />
pressure 57 [47][48].<br />
57 Acoustic, vibration or magnetic field sensors could detect the passage of vehicles and other equipment [46].<br />
58