National Mental Health Survey of India 2015-16
NMHS%20Report%20%28Mental%20Health%20Systems%29%201
NMHS%20Report%20%28Mental%20Health%20Systems%29%201
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
NMHS<br />
Information provided by States revealed that<br />
during the year <strong>2015</strong> the number <strong>of</strong> persons<br />
currently on treatment ranged between 8,446<br />
in Kerala to 8,50,000 in Gujarat (Alcohol use<br />
disorders - 11.7%, Neurotic disorders - 76%).<br />
The proportion <strong>of</strong> psychoses patients ranged<br />
from 6.4% in Punjab to 35.7% in Tamil Nadu.<br />
The burden <strong>of</strong> different types <strong>of</strong> mental<br />
disorders for most States based on routine<br />
HMIS is not presize as the HMIS provides data<br />
on persons seeking mental health care in public<br />
health system only. The burden <strong>of</strong> different<br />
types <strong>of</strong> mental disorders for Chhattisgarh,<br />
Jharkhand, Madhya Pradesh, Uttar Pradesh<br />
and West Bengal is not known, indicating<br />
that the HMIS systems for mental disorders is<br />
either not present or not standardised.<br />
5.11 <strong>Mental</strong> <strong>Health</strong> Legislation<br />
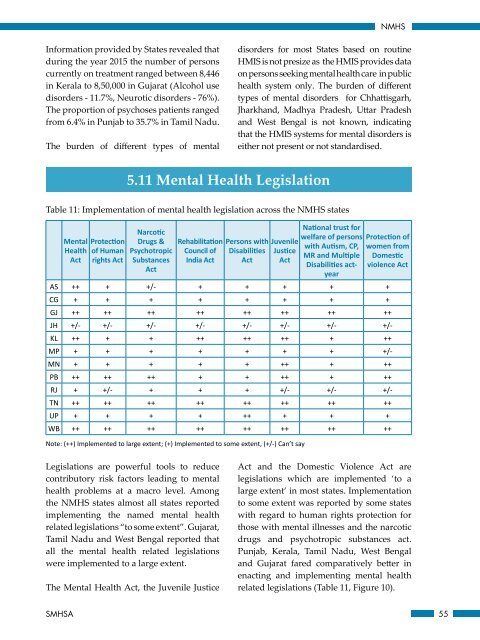
Table 11: Implementation <strong>of</strong> mental health legislation across the NMHS states<br />
<strong>Mental</strong><br />
<strong>Health</strong><br />
Act<br />
Protection<br />
<strong>of</strong> Human<br />
rights Act<br />
Narcotic<br />
Drugs &<br />
Psychotropic<br />
Substances<br />
Act<br />
Rehabilitation<br />
Council <strong>of</strong><br />
<strong>India</strong> Act<br />
Persons with<br />
Disabilities<br />
Act<br />
Juvenile<br />
Justice<br />
Act<br />
<strong>National</strong> trust for<br />
welfare <strong>of</strong> persons<br />
with Autism, CP,<br />
MR and Multiple<br />
Disabilities actyear<br />
Protection <strong>of</strong><br />
women from<br />
Domestic<br />
violence Act<br />
AS ++ + +/- + + + + +<br />
CG + + + + + + + +<br />
GJ ++ ++ ++ ++ ++ ++ ++ ++<br />
JH +/- +/- +/- +/- +/- +/- +/- +/-<br />
KL ++ + + ++ ++ ++ + ++<br />
MP + + + + + + + +/-<br />
MN + + + + + ++ + ++<br />
PB ++ ++ ++ + + ++ + ++<br />
RJ + +/- + + + +/- +/- +/-<br />
TN ++ ++ ++ ++ ++ ++ ++ ++<br />
UP + + + + ++ + + +<br />
WB ++ ++ ++ ++ ++ ++ ++ ++<br />
Note: (++) Implemented to large extent; (+) Implemented to some extent, (+/-) Can’t say<br />
Legislations are powerful tools to reduce<br />
contributory risk factors leading to mental<br />
health problems at a macro level. Among<br />
the NMHS states almost all states reported<br />
implementing the named mental health<br />
related legislations “to some extent”. Gujarat,<br />
Tamil Nadu and West Bengal reported that<br />
all the mental health related legislations<br />
were implemented to a large extent.<br />
The <strong>Mental</strong> <strong>Health</strong> Act, the Juvenile Justice<br />
Act and the Domestic Violence Act are<br />
legislations which are implemented ‘to a<br />
large extent’ in most states. Implementation<br />
to some extent was reported by some states<br />
with regard to human rights protection for<br />
those with mental illnesses and the narcotic<br />
drugs and psychotropic substances act.<br />
Punjab, Kerala, Tamil Nadu, West Bengal<br />
and Gujarat fared comparatively better in<br />
enacting and implementing mental health<br />
related legislations (Table 11, Figure 10).<br />
SMHSA<br />
55