2017 HCHB_digital
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
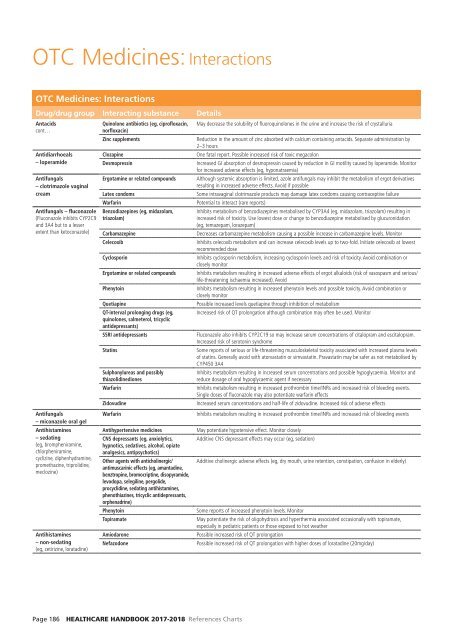
OTC Medicines: Interactions<br />
OTC Medicines: Interactions<br />
Drug/drug group Interacting substance Details<br />
Antacids<br />
cont…<br />
Antidiarrhoeals<br />
– loperamide<br />
Antifungals<br />
– clotrimazole vaginal<br />
cream<br />
Antifungals – fluconazole<br />
(Fluconazole inhibits CYP2C9<br />
and 3A4 but to a lesser<br />
extent than ketoconazole)<br />
Antifungals<br />
– miconazole oral gel<br />
Antihistamines<br />
– sedating<br />
(eg, brompheniramine,<br />
chlorpheniramine,<br />
cyclizine, diphenhydramine,<br />
promethazine, triprolidine,<br />
meclozine)<br />
Antihistamines<br />
– non-sedating<br />
(eg, cetirizine, loratadine)<br />
Quinolone antibiotics (eg, ciprofloxacin,<br />
norfloxacin)<br />
Zinc supplements<br />
Clozapine<br />
Desmopressin<br />
Ergotamine or related compounds<br />
Latex condoms<br />
Warfarin<br />
Benzodiazepines (eg, midazolam,<br />
triazolam)<br />
Carbamazepine<br />
Celecoxib<br />
Cyclosporin<br />
Ergotamine or related compounds<br />
Phenytoin<br />
Quetiapine<br />
QT-interval prolonging drugs (eg,<br />
quinolones, salmeterol, tricyclic<br />
antidepressants)<br />
SSRI antidepressants<br />
Statins<br />
Sulphonylureas and possibly<br />
thiazolidinediones<br />
Warfarin<br />
Zidovudine<br />
Warfarin<br />
Antihypertensive medicines<br />
CNS depressants (eg, anxiolytics,<br />
hypnotics, sedatives, alcohol, opiate<br />
analgesics, antipsychotics)<br />
Other agents with anticholinergic/<br />
antimuscarinic effects (eg, amantadine,<br />
benztropine, bromocriptine, disopyramide,<br />
levodopa, selegiline, pergolide,<br />
procyclidine, sedating antihistamines,<br />
phenothiazines, tricyclic antidepressants,<br />
orphenadrine)<br />
Phenytoin<br />
Topiramate<br />
Amiodarone<br />
Nefazodone<br />
May decrease the solubility of fluoroquinolones in the urine and increase the risk of crystalluria<br />
Reduction in the amount of zinc absorbed with calcium containing antacids. Separate administration by<br />
2–3 hours<br />
One fatal report. Possible increased risk of toxic megacolon<br />
Increased GI absorption of desmopressin caused by reduction in GI motility caused by loperamide. Monitor<br />
for increased adverse effects (eg, hyponatraemia)<br />
Although systemic absorption is limited, azole antifungals may inhibit the metabolism of ergot derivatives<br />
resulting in increased adverse effects. Avoid if possible<br />
Some intravaginal clotrimazole products may damage latex condoms causing contraceptive failure<br />
Potential to interact (rare reports)<br />
Inhibits metabolism of benzodiazepines metabolised by CYP3A4 (eg, midazolam, triazolam) resulting in<br />
increased risk of toxicity. Use lowest dose or change to benzodiazepine metabolised by glucuronidation<br />
(eg, temazepam, lorazepam)<br />
Decreases carbamazepine metabolism causing a possible increase in carbamazepine levels. Monitor<br />
Inhibits celecoxib metabolism and can increase celecoxib levels up to two-fold. Initiate celecoxib at lowest<br />
recommended dose<br />
Inhibits cyclosporin metabolism, increasing cyclosporin levels and risk of toxicity. Avoid combination or<br />
closely monitor<br />
Inhibits metabolism resulting in increased adverse effects of ergot alkaloids (risk of vasospasm and serious/<br />
life-threatening ischaemia increased). Avoid<br />
Inhibits metabolism resulting in increased phenytoin levels and possible toxicity. Avoid combination or<br />
closely monitor<br />
Possible increased levels quetiapine through inhibition of metabolism<br />
Increased risk of QT prolongation although combination may often be used. Monitor<br />
Fluconazole also inhibits CYP2C19 so may increase serum concentrations of citalopram and escitalopram.<br />
Increased risk of serotonin syndrome<br />
Some reports of serious or life-threatening musculoskeletal toxicity associated with increased plasma levels<br />
of statins. Generally avoid with atorvastatin or simvastatin. Pravastatin may be safer as not metabolised by<br />
CYP450 3A4<br />
Inhibits metabolism resulting in increased serum concentrations and possible hypoglycaemia. Monitor and<br />
reduce dosage of oral hypoglycaemic agent if necessary<br />
Inhibits metabolism resulting in increased prothrombin time/INRs and increased risk of bleeding events.<br />
Single doses of fluconazole may also potentiate warfarin effects<br />
Increased serum concentrations and half-life of zidovudine. Increased risk of adverse effects<br />
Inhibits metabolism resulting in increased prothrombin time/INRs and increased risk of bleeding events<br />
May potentiate hypotensive effect. Monitor closely<br />
Additive CNS depressant effects may occur (eg, sedation)<br />
Additive cholinergic adverse effects (eg, dry mouth, urine retention, constipation, confusion in elderly)<br />
Some reports of increased phenytoin levels. Monitor<br />
May potentiate the risk of oligohydrosis and hyperthermia associated occasionally with topiramate,<br />
especially in pediatric patients or those exposed to hot weather<br />
Possible increased risk of QT prolongation<br />
Possible increased risk of QT prolongation with higher doses of loratadine (20mg/day)<br />
Page 186 HEALTHCARE HANDBOOK <strong>2017</strong>-2018 References Charts