Single pull macgregor type hatch cover.pdf - Cochin University of ...
Single pull macgregor type hatch cover.pdf - Cochin University of ...
Single pull macgregor type hatch cover.pdf - Cochin University of ...
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
Longitudinal deformation <strong>of</strong> the top <strong>of</strong> the coaming is due to the hogging or<br />
sagging <strong>of</strong> the vessel. It depends on <strong>hatch</strong>way length and may be as much as 7-8 mm<br />
at each end. Longitudinal deformation is compensated for by fitting at the ends <strong>of</strong> the<br />
<strong>hatch</strong> <strong>cover</strong> with wide gaskets whose rubber absorbs the relative movement <strong>of</strong> the<br />
compression bars as the sip works. Hatch end cleats must allow such movements,<br />
which would otherwise be taken up at the cross joint with attendant risk <strong>of</strong> leakage.<br />
Steel to steel contact is must. The purpose <strong>of</strong> this is to prevent the over compression<br />
<strong>of</strong> the gaskets. However, it gives rise to a frictional force whose magnitude depends<br />
on the pressure <strong>of</strong> the <strong>cover</strong> on the coaming bar and their relative movement.<br />
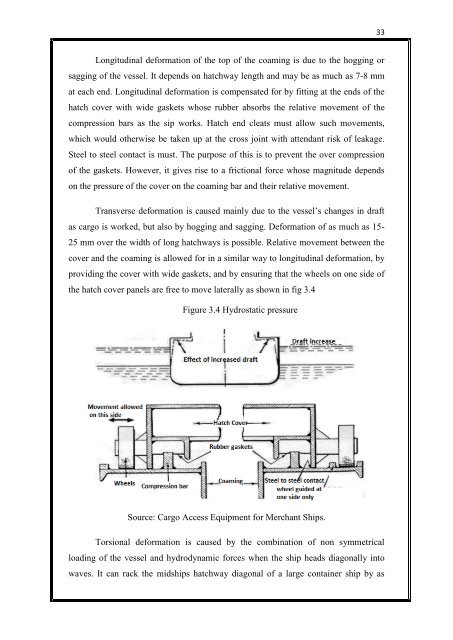
Transverse deformation is caused mainly due to the vessel’s changes in draft<br />
as cargo is worked, but also by hogging and sagging. Deformation <strong>of</strong> as much as 15-<br />
25 mm over the width <strong>of</strong> long <strong>hatch</strong>ways is possible. Relative movement between the<br />
<strong>cover</strong> and the coaming is allowed for in a similar way to longitudinal deformation, by<br />
providing the <strong>cover</strong> with wide gaskets, and by ensuring that the wheels on one side <strong>of</strong><br />
the <strong>hatch</strong> <strong>cover</strong> panels are free to move laterally as shown in fig 3.4<br />
Figure 3.4 Hydrostatic pressure<br />
Source: Cargo Access Equipment for Merchant Ships.<br />
Torsional deformation is caused by the combination <strong>of</strong> non symmetrical<br />
loading <strong>of</strong> the vessel and hydrodynamic forces when the ship heads diagonally into<br />
waves. It can rack the midships <strong>hatch</strong>way diagonal <strong>of</strong> a large container ship by as<br />
33