Confidence Intervals and Sample Size
Confidence Intervals and Sample Size
Confidence Intervals and Sample Size
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
lu49076_ch07.qxd 5/20/2003 3:15 PM Page 331<br />
Figure 7–2<br />
95% <strong>Confidence</strong> Interval<br />
for <strong>Sample</strong> Means<br />
Figure 7–3<br />
95% <strong>Confidence</strong> <strong>Intervals</strong><br />
for Each <strong>Sample</strong> Mean<br />
Section 7–2 <strong>Confidence</strong> <strong>Intervals</strong> for the Mean (s Known or n � 30) <strong>and</strong> <strong>Sample</strong> <strong>Size</strong> 331<br />
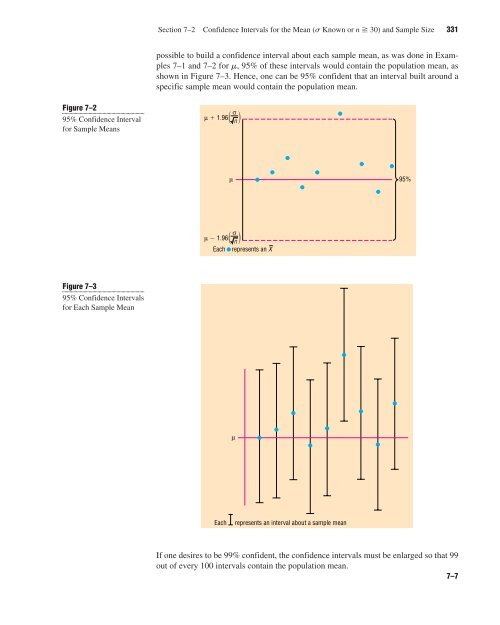
possible to build a confidence interval about each sample mean, as was done in Examples<br />
7–1 <strong>and</strong> 7–2 for m, 95% of these intervals would contain the population mean, as<br />
shown in Figure 7–3. Hence, one can be 95% confident that an interval built around a<br />
specific sample mean would contain the population mean.<br />
µ � 1.96<br />
σ<br />
( )<br />
µ<br />
n<br />
σ<br />
µ � 1.96( n )<br />
Each represents an X<br />
µ<br />
Each represents an interval about a sample mean<br />
If one desires to be 99% confident, the confidence intervals must be enlarged so that 99<br />
out of every 100 intervals contain the population mean.<br />
7–7<br />
95%