Section 3 (Crop Management)
Section 3 (Crop Management)
Section 3 (Crop Management)
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
Ameta and Sharma<br />
Table 5: Contribution of different legumes on fixation of atmospheric Nitrogen* under different<br />
intercropping treatments (kg/ha).<br />
Intercropping treatments Total N Total N Built up of soil Atmospheric N<br />
applied removed N<br />
fixed<br />
Maize-wheat (Check) 1800 2103 34 ---<br />
Maize+blackgram (paired rows in<br />
2:2 row ratio(30/90cm)-wheat<br />
1845 2475 181 128.0<br />
Maize+soybean (paired rows in 2:2<br />
row ratio(30/90cm)-wheat<br />
1860 2553 231 170.67<br />
Maize+pigeonpea-<br />
(Alternate rows in1:1 row<br />
ratio(30/30cm)-wheat<br />
1860 2490 118 111.67<br />
Maize+blackgram -(Alternate rows<br />
in1:1 row ratio(30/30cm)-wheat<br />
1845 2529 110 122.33<br />
* Computed from soil and plant analysis data of three year<br />
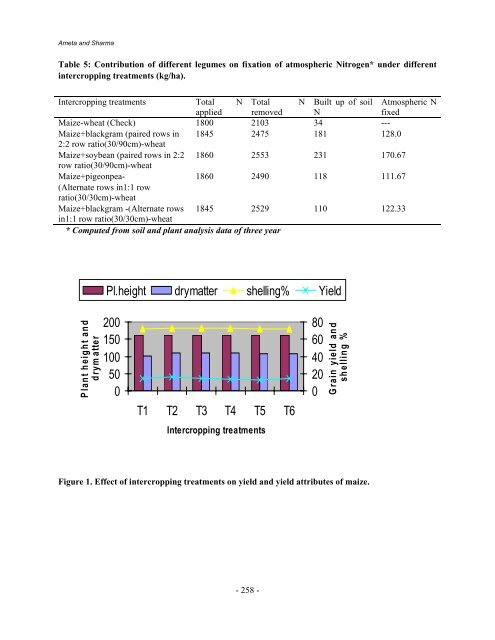
Plant height and<br />
drym atter<br />
Pl.height drymatter shelling% Yield<br />
200<br />
150<br />
100<br />
50<br />
0<br />
T1 T2 T3 T4 T5 T6<br />
Intercropping treatments<br />
80<br />
60<br />
40<br />
20<br />
0<br />
Grain yield and<br />
shelling %<br />
Figure 1. Effect of intercropping treatments on yield and yield attributes of maize.<br />
- 258 -