An innovative greywater treatment system for urban areas ... - SuSanA
An innovative greywater treatment system for urban areas ... - SuSanA
An innovative greywater treatment system for urban areas ... - SuSanA
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
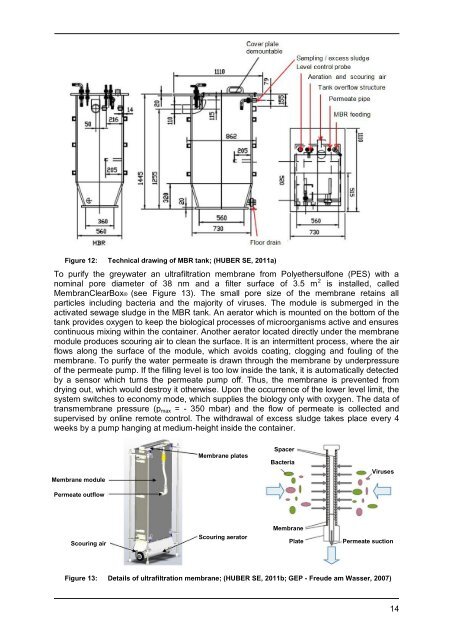
Figure 12: Technical drawing of MBR tank; (HUBER SE, 2011a)<br />
To purify the <strong>greywater</strong> an ultrafiltration membrane from Polyethersulfone (PES) with a<br />
nominal pore diameter of 38 nm and a filter surface of 3.5 m 2 is installed, called<br />
MembranClearBox® (see Figure 13). The small pore size of the membrane retains all<br />
particles including bacteria and the majority of viruses. The module is submerged in the<br />
activated sewage sludge in the MBR tank. <strong>An</strong> aerator which is mounted on the bottom of the<br />
tank provides oxygen to keep the biological processes of microorganisms active and ensures<br />
continuous mixing within the container. <strong>An</strong>other aerator located directly under the membrane<br />
module produces scouring air to clean the surface. It is an intermittent process, where the air<br />
flows along the surface of the module, which avoids coating, clogging and fouling of the<br />
membrane. To purify the water permeate is drawn through the membrane by underpressure<br />
of the permeate pump. If the filling level is too low inside the tank, it is automatically detected<br />
by a sensor which turns the permeate pump off. Thus, the membrane is prevented from<br />
drying out, which would destroy it otherwise. Upon the occurrence of the lower level limit, the<br />
<strong>system</strong> switches to economy mode, which supplies the biology only with oxygen. The data of<br />
transmembrane pressure (pmax = - 350 mbar) and the flow of permeate is collected and<br />
supervised by online remote control. The withdrawal of excess sludge takes place every 4<br />
weeks by a pump hanging at medium-height inside the container.<br />
Membrane module<br />
Permeate outflow<br />
Scouring air<br />
Membrane plates<br />
Scouring aerator<br />
Spacer<br />
Bacteria<br />
Membrane<br />
Viruses<br />
Plate Permeate suction<br />
Figure 13: Details of ultrafiltration membrane; (HUBER SE, 2011b; GEP - Freude am Wasser, 2007)<br />
14