Regulatory oversight of nuclear safety in Finland. Annual ... - STUK
Regulatory oversight of nuclear safety in Finland. Annual ... - STUK
Regulatory oversight of nuclear safety in Finland. Annual ... - STUK
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
Onkalo<br />
Posiva Oy is construct<strong>in</strong>g an<br />
underground research facility<br />
(Onkalo) <strong>in</strong> Olkiluoto, where<br />
bedrock volumes suitable for<br />
f<strong>in</strong>al disposal <strong>of</strong> spent <strong>nuclear</strong><br />
fuel can be <strong>in</strong>vestigated <strong>in</strong><br />
more detail. Bedrock research<br />
at the planned f<strong>in</strong>al disposal<br />
depth is a requirement for<br />
grant<strong>in</strong>g a construction<br />
licence for the f<strong>in</strong>al disposal<br />
facility. Posiva has designed<br />
Onkalo to function as one <strong>of</strong><br />
the entrance routes to the<br />
planned f<strong>in</strong>al disposal facility,<br />
so <strong>STUK</strong> is apply<strong>in</strong>g<br />
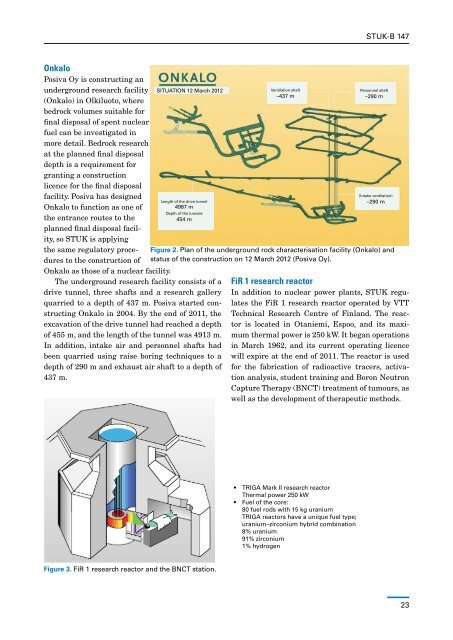
SITUATION 12 March 2012<br />
Length <strong>of</strong> the drive tunnel<br />
4987 m<br />
Depth <strong>of</strong> the tunnels<br />
454 m<br />
the same regulatory procedures<br />
to the construction <strong>of</strong><br />
Onkalo as those <strong>of</strong> a <strong>nuclear</strong> facility.<br />
The underground research facility consists <strong>of</strong> a<br />
drive tunnel, three shafts and a research gallery<br />
quarried to a depth <strong>of</strong> 437 m. Posiva started construct<strong>in</strong>g<br />
Onkalo <strong>in</strong> 2004. By the end <strong>of</strong> 2011, the<br />
excavation <strong>of</strong> the drive tunnel had reached a depth<br />
<strong>of</strong> 455 m, and the length <strong>of</strong> the tunnel was 4913 m.<br />
In addition, <strong>in</strong>take air and personnel shafts had<br />
been quarried us<strong>in</strong>g raise bor<strong>in</strong>g techniques to a<br />
depth <strong>of</strong> 290 m and exhaust air shaft to a depth <strong>of</strong><br />
437 m.<br />
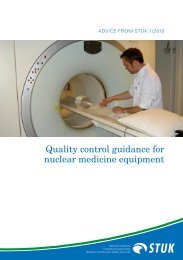
Figure 3. FiR 1 research reactor and the BNCT station.<br />
Ventilation shaft<br />
–437 m<br />
• TRIGA Mark II research reactor<br />
Thermal power 250 kW<br />
• Fuel <strong>of</strong> the core:<br />
80 fuel rods with 15 kg uranium<br />
TRIGA reactors have a unique fuel type;<br />
uranium–zirconium hybrid comb<strong>in</strong>ation<br />
8% uranium<br />
91% zirconium<br />
1% hydrogen<br />
<strong>STUK</strong>-B 147<br />
Personnel shaft<br />
–290 m<br />
(Intake ventilation)<br />
–290 m<br />
Figure 2. Plan <strong>of</strong> the underground rock characterisation facility (Onkalo) and<br />
status <strong>of</strong> the construction on 12 March 2012 (Posiva Oy).<br />
FiR 1 research reactor<br />
In addition to <strong>nuclear</strong> power plants, <strong>STUK</strong> regulates<br />
the FiR 1 research reactor operated by VTT<br />
Technical Research Centre <strong>of</strong> F<strong>in</strong>land. The reactor<br />
is located <strong>in</strong> Otaniemi, Espoo, and its maximum<br />
thermal power is 250 kW. It began operations<br />
<strong>in</strong> March 1962, and its current operat<strong>in</strong>g licence<br />
will expire at the end <strong>of</strong> 2011. The reactor is used<br />
for the fabrication <strong>of</strong> radioactive tracers, activation<br />
analysis, student tra<strong>in</strong><strong>in</strong>g and Boron Neutron<br />
Capture Therapy (BNCT) treatment <strong>of</strong> tumours, as<br />
well as the development <strong>of</strong> therapeutic methods.<br />
23