Capīıtulo 3 Rotación de moléculas poliatómicas
Capīıtulo 3 Rotación de moléculas poliatómicas
Capīıtulo 3 Rotación de moléculas poliatómicas
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
L3: <strong>Rotación</strong> <strong>de</strong> <strong>moléculas</strong> <strong>poliatómicas</strong> Mecánica clásica <strong>de</strong> un rotor rígido<br />
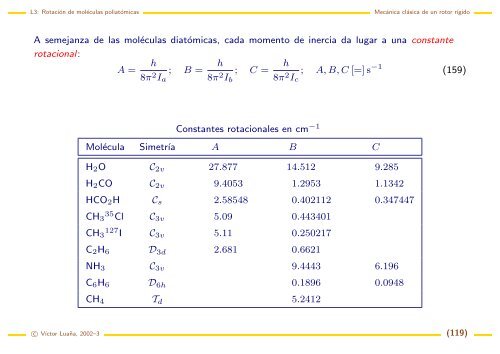
A semejanza <strong>de</strong> las <strong>moléculas</strong> diatómicas, cada momento <strong>de</strong> inercia da lugar a una constante<br />
rotacional:<br />
A =<br />
h<br />
8π2 ; B =<br />
Ia<br />
h<br />
8π2 ; C =<br />
Ib<br />
h<br />
8π2 ; A, B, C [=] s<br />
Ic<br />
−1<br />
(159)<br />
Constantes rotacionales en cm −1<br />
Molécula Simetría A B C<br />
H2O C2v 27.877 14.512 9.285<br />
H2CO C2v 9.4053 1.2953 1.1342<br />
HCO2H Cs 2.58548 0.402112 0.347447<br />
CH3 35 Cl C3v 5.09 0.443401<br />
CH3 127 I C3v 5.11 0.250217<br />
C2H6 D3d 2.681 0.6621<br />
NH3 C3v 9.4443 6.196<br />
C6H6 D6h 0.1896 0.0948<br />
CH4 Td 5.2412<br />
c○ Víctor Luaña, 2002–3 (119)