Dryandra Woodland - Department of Environment and Conservation ...
Dryandra Woodland - Department of Environment and Conservation ...
Dryandra Woodland - Department of Environment and Conservation ...
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
20. WEEDS<br />
BACKGROUND<br />
A weed is defined as a plant or species growing out <strong>of</strong> place. When growing in native bushl<strong>and</strong>, an<br />
unwanted plant is called a bushl<strong>and</strong> or environmental weed.<br />
Weeds may cause major structural change to native plant communities, altering flammability,<br />
displacing threatened species <strong>and</strong> regenerating seedlings, dispossessing native animals <strong>of</strong> habitat or<br />
food, <strong>and</strong> changing ecosystem processes such as the cycling <strong>of</strong> water or nutrients.<br />
Healthy native vegetation is normally able to resist invasion <strong>of</strong> weeds. Most weeds require certain<br />
conditions, including the opening up <strong>of</strong> the canopy, soil disturbance or influx <strong>of</strong> nutrients before<br />
they can spread.<br />
The major source <strong>of</strong> weeds at <strong>Dry<strong>and</strong>ra</strong> is from adjacent l<strong>and</strong>s. Major routes <strong>of</strong> spread are across<br />
private property boundaries, along linear disturbance features such as roads, tracks, <strong>and</strong> railway<br />
formations, <strong>and</strong> along creeklines. Weed dispersal can be increased by vectors including vehicles <strong>and</strong><br />
machinery, soil movement, <strong>and</strong> by native <strong>and</strong> domestic animals.<br />
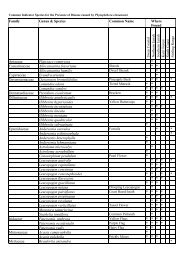
Of the 890 plant species recorded within the <strong>Woodl<strong>and</strong></strong>, 74 are introduced (38 monocotyledons <strong>and</strong><br />
36 dicotyledons). Of these, the cape tulips (Homeria flaccida <strong>and</strong> H. collina) are declared category<br />
P3 weeds under the Agriculture <strong>and</strong> Related Resources Protection Act 1976. Category P3 plants are<br />
those where the numbers <strong>of</strong> plants or distribution, or both, should be reduced. Soursob (Oxalis<br />
pes-caprae) is declared P4, ie. those plants that should be prevented from spreading beyond their<br />
present distribution.<br />
Some areas, such as creeklines <strong>and</strong> granite outcrops, are highly susceptible to weed spread due to the<br />
high water <strong>and</strong> nutrient status <strong>of</strong> these sites. Weed propagules can also be carried down streamlines<br />
by water. Most <strong>of</strong> <strong>Dry<strong>and</strong>ra</strong> is upl<strong>and</strong>s; consequently weed spread by this route is slow. However,<br />
upstream spread <strong>of</strong> cape tulip, Guildford grass (Romulea rosea), Cape Weed (Arctotheca calendula),<br />
clovers (Trifolium species) <strong>and</strong> Soursob is occurring on some <strong>of</strong> the creeklines.<br />
Grasses such as veldt grass (Ehrharta species), wild oats (Avena species) <strong>and</strong> African Love Grass<br />
(Eragrostis curvula) can increase the fire hazard <strong>and</strong> out compete native vegetation for water <strong>and</strong><br />
nutrients.<br />
Other weeds such as Bridal Creeper (Myrsiphyllum asparagoides), watsonia (Watsonia species),<br />
Freesias (Freesia leichtlinii) <strong>and</strong> perennial grasses are not yet a problem in <strong>Dry<strong>and</strong>ra</strong>; however, they<br />
do pose a threat to native vegetation because <strong>of</strong> their ability to invade <strong>and</strong> then dominate native plant<br />
communities.<br />
79