shot peening residual stress - Metal Improvement Company
shot peening residual stress - Metal Improvement Company
shot peening residual stress - Metal Improvement Company
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
C H A P T E R T W O<br />
RESPONSE OF METALS<br />
14<br />
T I T A N I U M<br />
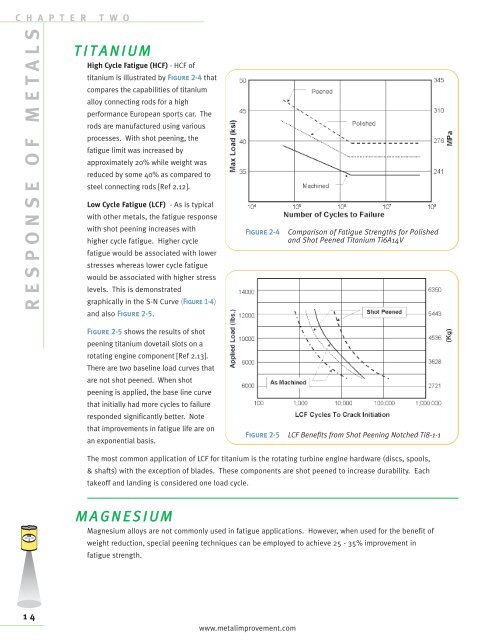
High Cycle Fatigue (HCF) - HCF of<br />
titanium is illustrated by Figure 2-4 that<br />
compares the capabilities of titanium<br />
alloy connecting rods for a high<br />
performance European sports car. The<br />
rods are manufactured using various<br />
processes. With <strong>shot</strong> <strong>peening</strong>, the<br />
fatigue limit was increased by<br />
approximately 20% while weight was<br />
reduced by some 40% as compared to<br />
steel connecting rods [Ref 2.12].<br />
Low Cycle Fatigue (LCF) - As is typical<br />
with other metals, the fatigue response<br />
with <strong>shot</strong> <strong>peening</strong> increases with<br />
higher cycle fatigue. Higher cycle<br />
fatigue would be associated with lower<br />
<strong>stress</strong>es whereas lower cycle fatigue<br />
would be associated with higher <strong>stress</strong><br />
levels. This is demonstrated<br />
graphically in the S-N Curve (Figure 1-4)<br />
and also Figure 2-5.<br />
Figure 2-5 shows the results of <strong>shot</strong><br />
<strong>peening</strong> titanium dovetail slots on a<br />
rotating engine component [Ref 2.13].<br />
There are two baseline load curves that<br />
are not <strong>shot</strong> peened. When <strong>shot</strong><br />
<strong>peening</strong> is applied, the base line curve<br />
that initially had more cycles to failure<br />
responded significantly better. Note<br />
that improvements in fatigue life are on<br />
an exponential basis.<br />
Figure 2-4 Comparison of Fatigue Strengths for Polished<br />
and Shot Peened Titanium Ti6A14V<br />
Figure 2-5 LCF Benefits from Shot Peening Notched Ti8-1-1<br />
The most common application of LCF for titanium is the rotating turbine engine hardware (discs, spools,<br />
& shafts) with the exception of blades. These components are <strong>shot</strong> peened to increase durability. Each<br />
takeoff and landing is considered one load cycle.<br />
M A G N E S I U M<br />
Magnesium alloys are not commonly used in fatigue applications. However, when used for the benefit of<br />
weight reduction, special <strong>peening</strong> techniques can be employed to achieve 25 - 35% improvement in<br />
fatigue strength.<br />
www.metalimprovement.com