EU industrial structure - EU Bookshop - Europa
EU industrial structure - EU Bookshop - Europa
EU industrial structure - EU Bookshop - Europa
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
<strong>EU</strong> <strong>industrial</strong> <strong>structure</strong> 2011 — Trends and Performance<br />
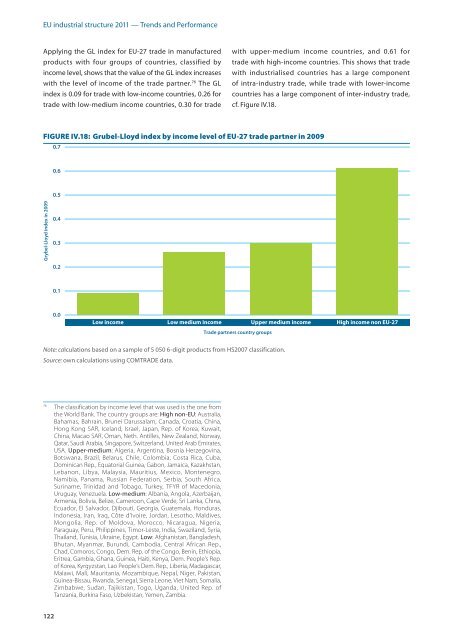
Applying the GL index for <strong>EU</strong>‑27 trade in manufactured<br />
products with four groups of countries, classified by<br />
income level, shows that the value of the GL index increases<br />
with the level of income of the trade partner. 76 The GL<br />
index is 0.09 for trade with low‑income countries, 0.26 for<br />
trade with low‑medium income countries, 0.30 for trade<br />
76 The classification by income level that was used is the one from<br />
the World Bank. The country groups are: High non‑<strong>EU</strong>: Australia,<br />
Bahamas, Bahrain, Brunei Darussalam, Canada, Croatia, China,<br />
Hong Kong SAR, Iceland, Israel, Japan, Rep. of Korea, Kuwait,<br />
China, Macao SAR, Oman, Neth. Antilles, New Zealand, Norway,<br />
Qatar, Saudi Arabia, Singapore, Switzerland, United Arab Emirates,<br />
USA. Upper‑medium: Algeria, Argentina, Bosnia Herzegovina,<br />
Botswana, Brazil, Belarus, Chile, Colombia, Costa Rica, Cuba,<br />
Dominican Rep., Equatorial Guinea, Gabon, Jamaica, Kazakhstan,<br />
Lebanon, Libya, Malaysia, Mauritius, Mexico, Montenegro,<br />
Namibia, Panama, Russian Federation, Serbia, South Africa,<br />
Suriname, Trinidad and Tobago, Turkey, TFYR of Macedonia,<br />
Uruguay, Venezuela. Low‑medium: Albania, Angola, Azerbaijan,<br />
Armenia, Bolivia, Belize, Cameroon, Cape Verde, Sri Lanka, China,<br />
Ecuador, El Salvador, Djibouti, Georgia, Guatemala, Honduras,<br />
Indonesia, Iran, Iraq, Côte d’Ivoire, Jordan, Lesotho, Maldives,<br />
Mongolia, Rep. of Moldova, Morocco, Nicaragua, Nigeria,<br />
Paraguay, Peru, Philippines, Timor-Leste, India, Swaziland, Syria,<br />
Thailand, Tunisia, Ukraine, Egypt. Low: Afghanistan, Bangladesh,<br />
Bhutan, Myanmar, Burundi, Cambodia, Central African Rep.,<br />
Chad, Comoros, Congo, Dem. Rep. of the Congo, Benin, Ethiopia,<br />
Eritrea, Gambia, Ghana, Guinea, Haiti, Kenya, Dem. People’s Rep.<br />
of Korea, Kyrgyzstan, Lao People’s Dem. Rep., Liberia, Madagascar,<br />
Malawi, Mali, Mauritania, Mozambique, Nepal, Niger, Pakistan,<br />
Guinea-Bissau, Rwanda, Senegal, Sierra Leone, Viet Nam, Somalia,<br />
Zimbabwe, Sudan, Tajikistan, Togo, Uganda, United Rep. of<br />
Tanzania, Burkina Faso, Uzbekistan, Yemen, Zambia.<br />
122<br />
with upper‑medium income countries, and 0.61 for<br />
trade with high‑income countries. This shows that trade<br />
with <strong>industrial</strong>ised countries has a large component<br />
of intra‑industry trade, while trade with lower‑income<br />
countries has a large component of inter‑industry trade,<br />
cf. Figure IV.18.<br />
FIgURE IV.18: grubel-Lloyd index by income level of <strong>EU</strong>-27 trade partner in 2009<br />
Grybel-Lloyd index in 2009<br />
0.7<br />
0.6<br />
0.5<br />
0.4<br />
0.3<br />
0.2<br />
0.1<br />
0.0<br />
Low income<br />
Low medium income<br />
Trade partners country groups<br />
Upper medium income<br />
Note: calculations based on a sample of 5 050 6‑digit products from HS2007 classification.<br />
Source: own calculations using COMTRADE data.<br />
High income non <strong>EU</strong>-27