EU industrial structure - EU Bookshop - Europa
EU industrial structure - EU Bookshop - Europa
EU industrial structure - EU Bookshop - Europa
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
Chapter III — Drivers of Sector Growth and Competitiveness<br />
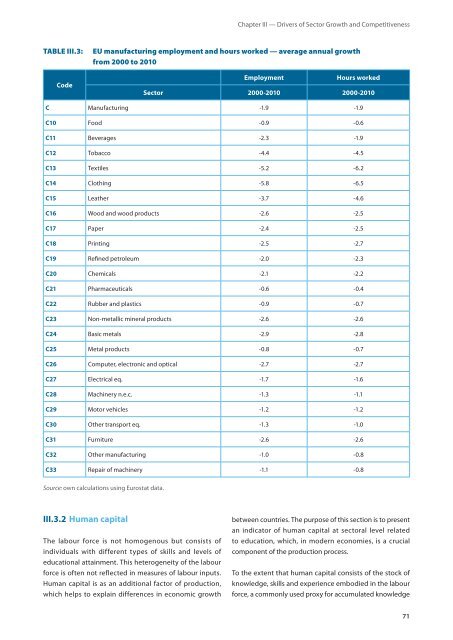
TAbLE III.3: <strong>EU</strong> manufacturing employment and hours worked — average annual growth<br />
from 2000 to 2010<br />
code<br />
Employment hours worked<br />
sector 2000‑2010 2000‑2010<br />
c Manufacturing ‑1.9 ‑1.9<br />
c10 Food ‑0.9 ‑0.6<br />
c11 Beverages ‑2.3 ‑1.9<br />
c12 Tobacco ‑4.4 ‑4.5<br />
c13 Textiles ‑5.2 ‑6.2<br />
c14 Clothing ‑5.8 ‑6.5<br />
c15 Leather ‑3.7 ‑4.6<br />
c16 Wood and wood products ‑2.6 ‑2.5<br />
c17 Paper ‑2.4 ‑2.5<br />
c18 Printing ‑2.5 ‑2.7<br />
c19 Refined petroleum ‑2.0 ‑2.3<br />
c20 Chemicals ‑2.1 ‑2.2<br />
c21 Pharmaceuticals ‑0.6 ‑0.4<br />
c22 Rubber and plastics ‑0.9 ‑0.7<br />
c23 Non‑metallic mineral products ‑2.6 ‑2.6<br />
c24 Basic metals ‑2.9 ‑2.8<br />
c25 Metal products ‑0.8 ‑0.7<br />
c26 Computer, electronic and optical ‑2.7 ‑2.7<br />
c27 Electrical eq. ‑1.7 ‑1.6<br />
c28 Machinery n.e.c. ‑1.3 ‑1.1<br />
c29 Motor vehicles ‑1.2 ‑1.2<br />
c30 Other transport eq. ‑1.3 ‑1.0<br />
c31 Furniture ‑2.6 ‑2.6<br />
c32 Other manufacturing ‑1.0 ‑0.8<br />
c33 Repair of machinery ‑1.1 ‑0.8<br />
Source: own calculations using Eurostat data.<br />
iii32 human capital<br />
The labour force is not homogenous but consists of<br />
individuals with different types of skills and levels of<br />
educational attainment. This heterogeneity of the labour<br />
force is often not reflected in measures of labour inputs.<br />
Human capital is as an additional factor of production,<br />
which helps to explain differences in economic growth<br />
between countries. The purpose of this section is to present<br />
an indicator of human capital at sectoral level related<br />
to education, which, in modern economies, is a crucial<br />
component of the production process.<br />
To the extent that human capital consists of the stock of<br />
knowledge, skills and experience embodied in the labour<br />
force, a commonly used proxy for accumulated knowledge<br />
71