Progressively Interactive Evolutionary Multi-Objective Optimization ...
Progressively Interactive Evolutionary Multi-Objective Optimization ...
Progressively Interactive Evolutionary Multi-Objective Optimization ...
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
F2<br />
0.4<br />
0.2<br />
0<br />
−0.2<br />
Lower level P−O front<br />
y1=0.001<br />
(u1(y1), u2(y1))<br />
−0.4<br />
Upper level<br />
P−O front<br />
−0.6<br />
y1=1<br />
−0.8 Most Preferred<br />
Point<br />
−1<br />
−0.2 0 0.2 0.4 0.6 0.8<br />
F1<br />
1<br />
1.2<br />
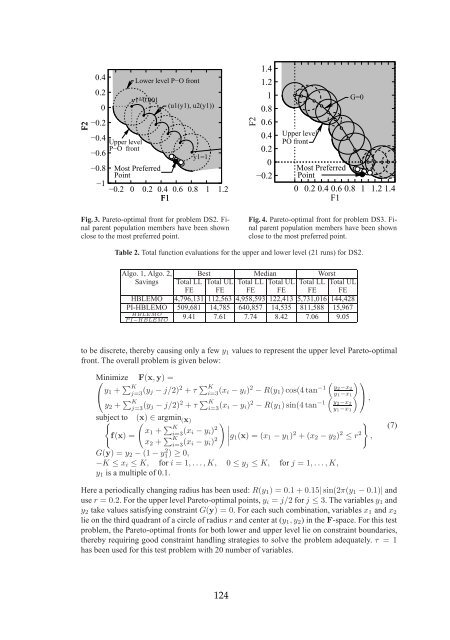
Fig. 3. Pareto-optimal front for problem DS2. Final<br />
parent population members have been shown<br />
close to the most preferred point.<br />
F2<br />
1.4<br />
1.2<br />
1<br />
0.8<br />
0.6<br />
0.4<br />
0.2<br />
0<br />
−0.2<br />
Upper level<br />
PO front<br />
Most Preferred<br />
Point<br />
G=0<br />
0 0.2 0.4 0.6 0.8 1 1.2 1.4<br />
F1<br />
Fig. 4. Pareto-optimal front for problem DS3. Final<br />
parent population members have been shown<br />
close to the most preferred point.<br />
Table 2. Total function evaluations for the upper and lower level (21 runs) for DS2.<br />
Algo. 1, Algo. 2, Best Median Worst<br />
Savings Total LL Total UL Total LL Total UL Total LL Total UL<br />
FE FE FE FE FE FE<br />
HBLEMO 4,796,131 112,563 4,958,593 122,413 5,731,016 144,428<br />
PI-HBLEMO 509,681 14,785 640,857 14,535 811,588 15,967<br />
HBLEMO<br />
P I−HBLEMO 9.41 7.61 7.74 8.42 7.06 9.05<br />
to be discrete, thereby causing only a few y1 values to represent the upper level Pareto-optimal<br />
front. The overall problem is given below:<br />
⎛Minimize<br />
F(x, y) =<br />
⎝ y1 + K j=3 (yj − j/2) 2 + τ K i=3 (xi − yi) 2 − R(y1) cos(4 tan−1 y2−x2<br />
y1−x1<br />
y2 + K j=3 (yj − j/2) 2 + τ K i=3 (xi − yi) 2 − R(y1) sin(4 tan−1 <br />
y2−x2<br />
y1−x1<br />
⎞<br />
⎠ ,<br />
subject<br />
<br />
to (x)<br />
<br />
∈ argmin (x)<br />
x1 +<br />
f(x) =<br />
K i=3 (xi − yi) 2<br />
x2 + K i=3 (xi − yi) 2<br />
<br />
g1(x) = (x1 − y1) 2 + (x2 − y2) 2 ≤ r2 <br />
,<br />
G(y) = y2 − (1 − y2 1 ) ≥ 0,<br />
−K ≤ xi ≤ K, for i = 1, . . . , K, 0 ≤ yj ≤ K, for j = 1, . . . , K,<br />
y1 is a multiple of 0.1.<br />
Here a periodically changing radius has been used: R(y1) = 0.1 + 0.15| sin(2π(y1 − 0.1)| and<br />
use r = 0.2. For the upper level Pareto-optimal points, yi = j/2 for j ≤ 3. The variables y1 and<br />
y2 take values satisfying constraint G(y) = 0. For each such combination, variables x1 and x2<br />
lie on the third quadrant of a circle of radius r and center at (y1, y2) in the F-space. For this test<br />
problem, the Pareto-optimal fronts for both lower and upper level lie on constraint boundaries,<br />
thereby requiring good constraint handling strategies to solve the problem adequately. τ = 1<br />
has been used for this test problem with 20 number of variables.<br />
124<br />
(7)