GM Crops: The First Ten Years - International Service for the ...
GM Crops: The First Ten Years - International Service for the ...
GM Crops: The First Ten Years - International Service for the ...
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
<strong>GM</strong> <strong>Crops</strong>: <strong>The</strong> <strong>First</strong> <strong>Ten</strong> <strong>Years</strong><br />
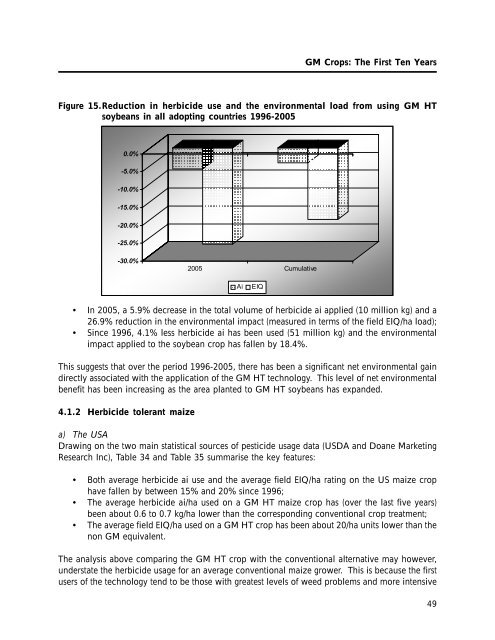
Figure 15.Reduction in herbicide use and <strong>the</strong> environmental load from using <strong>GM</strong> HT<br />
soybeans in all adopting countries 1996-2005<br />
0.0%<br />
-5.0%<br />
-10.0%<br />
-15.0%<br />
-20.0%<br />
-25.0%<br />
-30.0%<br />
• In 2005, a 5.9% decrease in <strong>the</strong> total volume of herbicide ai applied (10 million kg) and a<br />
26.9% reduction in <strong>the</strong> environmental impact (measured in terms of <strong>the</strong> field EIQ/ha load);<br />
• Since 1996, 4.1% less herbicide ai has been used (51 million kg) and <strong>the</strong> environmental<br />
impact applied to <strong>the</strong> soybean crop has fallen by 18.4%.<br />
This suggests that over <strong>the</strong> period 1996-2005, <strong>the</strong>re has been a significant net environmental gain<br />
directly associated with <strong>the</strong> application of <strong>the</strong> <strong>GM</strong> HT technology. This level of net environmental<br />
benefit has been increasing as <strong>the</strong> area planted to <strong>GM</strong> HT soybeans has expanded.<br />
4.1.2 Herbicide tolerant maize<br />
2005 Cumulative<br />
Ai EIQ<br />
a) <strong>The</strong> USA<br />
Drawing on <strong>the</strong> two main statistical sources of pesticide usage data (USDA and Doane Marketing<br />
Research Inc), Table 34 and Table 35 summarise <strong>the</strong> key features:<br />
• Both average herbicide ai use and <strong>the</strong> average field EIQ/ha rating on <strong>the</strong> US maize crop<br />
have fallen by between 15% and 20% since 1996;<br />
• <strong>The</strong> average herbicide ai/ha used on a <strong>GM</strong> HT maize crop has (over <strong>the</strong> last five years)<br />
been about 0.6 to 0.7 kg/ha lower than <strong>the</strong> corresponding conventional crop treatment;<br />
• <strong>The</strong> average field EIQ/ha used on a <strong>GM</strong> HT crop has been about 20/ha units lower than <strong>the</strong><br />
non <strong>GM</strong> equivalent.<br />
<strong>The</strong> analysis above comparing <strong>the</strong> <strong>GM</strong> HT crop with <strong>the</strong> conventional alternative may however,<br />
understate <strong>the</strong> herbicide usage <strong>for</strong> an average conventional maize grower. This is because <strong>the</strong> first<br />
users of <strong>the</strong> technology tend to be those with greatest levels of weed problems and more intensive<br />
49