GM Crops: The First Ten Years - International Service for the ...
GM Crops: The First Ten Years - International Service for the ...
GM Crops: The First Ten Years - International Service for the ...
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
<strong>GM</strong> <strong>Crops</strong>: <strong>The</strong> <strong>First</strong> <strong>Ten</strong> <strong>Years</strong><br />
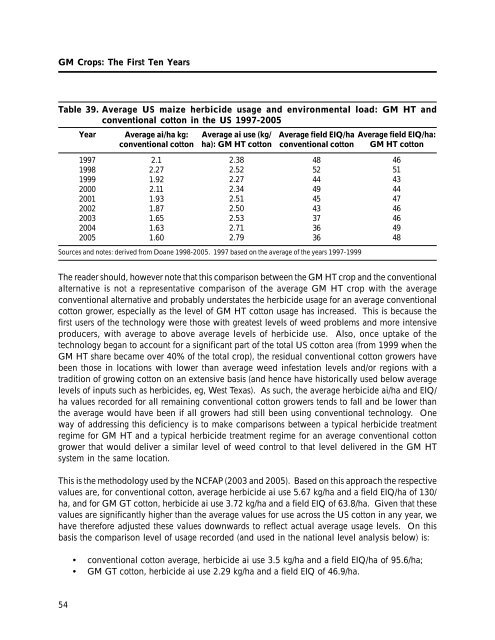
Table 39. Average US maize herbicide usage and environmental load: <strong>GM</strong> HT and<br />
conventional cotton in <strong>the</strong> US 1997-2005<br />
Year Average ai/ha kg: Average ai use (kg/<br />
conventional cotton ha): <strong>GM</strong> HT cotton<br />
1997<br />
1998<br />
1999<br />
2000<br />
2001<br />
2002<br />
2003<br />
2004<br />
2005<br />
2.1<br />
2.27<br />
1.92<br />
2.11<br />
1.93<br />
1.87<br />
1.65<br />
1.63<br />
1.60<br />
2.38<br />
2.52<br />
2.27<br />
2.34<br />
2.51<br />
2.50<br />
2.53<br />
2.71<br />
2.79<br />
Average field EIQ/ha<br />
conventional cotton<br />
Sources and notes: derived from Doane 1998-2005. 1997 based on <strong>the</strong> average of <strong>the</strong> years 1997-1999<br />
48<br />
52<br />
44<br />
49<br />
45<br />
43<br />
37<br />
36<br />
36<br />
Average field EIQ/ha:<br />
<strong>GM</strong> HT cotton<br />
<strong>The</strong> reader should, however note that this comparison between <strong>the</strong> <strong>GM</strong> HT crop and <strong>the</strong> conventional<br />
alternative is not a representative comparison of <strong>the</strong> average <strong>GM</strong> HT crop with <strong>the</strong> average<br />
conventional alternative and probably understates <strong>the</strong> herbicide usage <strong>for</strong> an average conventional<br />
cotton grower, especially as <strong>the</strong> level of <strong>GM</strong> HT cotton usage has increased. This is because <strong>the</strong><br />
first users of <strong>the</strong> technology were those with greatest levels of weed problems and more intensive<br />
producers, with average to above average levels of herbicide use. Also, once uptake of <strong>the</strong><br />
technology began to account <strong>for</strong> a significant part of <strong>the</strong> total US cotton area (from 1999 when <strong>the</strong><br />
<strong>GM</strong> HT share became over 40% of <strong>the</strong> total crop), <strong>the</strong> residual conventional cotton growers have<br />
been those in locations with lower than average weed infestation levels and/or regions with a<br />
tradition of growing cotton on an extensive basis (and hence have historically used below average<br />
levels of inputs such as herbicides, eg, West Texas). As such, <strong>the</strong> average herbicide ai/ha and EIQ/<br />
ha values recorded <strong>for</strong> all remaining conventional cotton growers tends to fall and be lower than<br />
<strong>the</strong> average would have been if all growers had still been using conventional technology. One<br />
way of addressing this deficiency is to make comparisons between a typical herbicide treatment<br />
regime <strong>for</strong> <strong>GM</strong> HT and a typical herbicide treatment regime <strong>for</strong> an average conventional cotton<br />
grower that would deliver a similar level of weed control to that level delivered in <strong>the</strong> <strong>GM</strong> HT<br />
system in <strong>the</strong> same location.<br />
This is <strong>the</strong> methodology used by <strong>the</strong> NCFAP (2003 and 2005). Based on this approach <strong>the</strong> respective<br />
values are, <strong>for</strong> conventional cotton, average herbicide ai use 5.67 kg/ha and a field EIQ/ha of 130/<br />
ha, and <strong>for</strong> <strong>GM</strong> GT cotton, herbicide ai use 3.72 kg/ha and a field EIQ of 63.8/ha. Given that <strong>the</strong>se<br />
values are significantly higher than <strong>the</strong> average values <strong>for</strong> use across <strong>the</strong> US cotton in any year, we<br />
have <strong>the</strong>re<strong>for</strong>e adjusted <strong>the</strong>se values downwards to reflect actual average usage levels. On this<br />
basis <strong>the</strong> comparison level of usage recorded (and used in <strong>the</strong> national level analysis below) is:<br />
54<br />
• conventional cotton average, herbicide ai use 3.5 kg/ha and a field EIQ/ha of 95.6/ha;<br />
• <strong>GM</strong> GT cotton, herbicide ai use 2.29 kg/ha and a field EIQ of 46.9/ha.<br />
46<br />
51<br />
43<br />
44<br />
47<br />
46<br />
46<br />
49<br />
48