Hyperbare Zuurstoftherapie: Rapid Assessment - KCE
Hyperbare Zuurstoftherapie: Rapid Assessment - KCE
Hyperbare Zuurstoftherapie: Rapid Assessment - KCE
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
20 Hyperbaric Oxygenation Therapy <strong>KCE</strong> Reports 74<br />
After the introduction of recompression therapy with air, symptoms dramatically<br />
improved. In combination with other improvements at the worksite mortality fell to less<br />
than 2% annually. 4 More recent studies in workers with caisson disease also show the<br />
high effectiveness of recompression therapy. 44<br />
Therefore, most current recommendations and recent RCTs deal mainly with different<br />
therapy schedules and adjuvant therapies. Besides, specific guidelines for the prevention<br />
of DCS in divers, both professional and recreational, and in professionals working in<br />
hyperbaric conductions have been elaborated. Details of these are outside the scope of<br />
1, 8, 9<br />
this report but can be found in the relevant publications.<br />
Several hyperbaric schedules have been described and tested, differing in pressure, time,<br />
frequency and number of sessions, and although there are no human RCTs available<br />
comparing HBOT to no HBOT it is generally agreed that early hyperbaric treatment is<br />
most likely to lead to complete recovery in mild or moderate DCS. 8 Conducting RCTs<br />
of HBOT versus a sham alternative is considered by many in the field as unethical, but<br />
they agree that there is definitely a need for rigorous RCTs to define optimal treatment<br />
schedules, adjuvant therapy and potentially the use of gas mixtures other than 100%<br />
oxygen. 45<br />
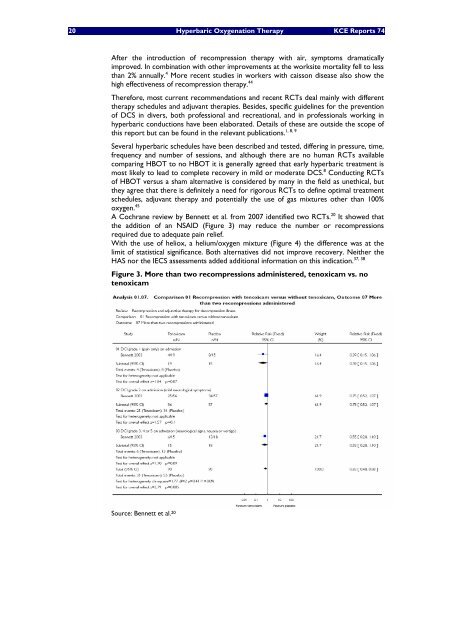
A Cochrane review by Bennett et al. from 2007 identified two RCTs. 20 It showed that<br />
the addition of an NSAID (Figure 3) may reduce the number or recompressions<br />
required due to adequate pain relief.<br />
With the use of heliox, a helium/oxygen mixture (Figure 4) the difference was at the<br />
limit of statistical significance. Both alternatives did not improve recovery. Neither the<br />
37, 38<br />
HAS nor the IECS assessments added additional information on this indication.<br />
Figure 3. More than two recompressions administered, tenoxicam vs. no<br />
tenoxicam<br />
Source: Bennett et al. 20