Student Resources—746
Student Resources—746
Student Resources—746
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
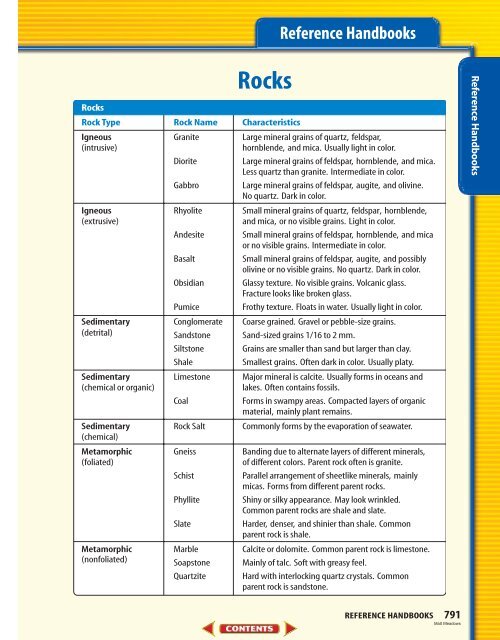
Rocks<br />
Rocks<br />
Rock Type Rock Name Characteristics<br />
Reference Handbooks<br />
Igneous Granite Large mineral grains of quartz, feldspar,<br />
(intrusive) hornblende, and mica. Usually light in color.<br />
Diorite Large mineral grains of feldspar, hornblende, and mica.<br />
Less quartz than granite. Intermediate in color.<br />
Gabbro Large mineral grains of feldspar, augite, and olivine.<br />
No quartz. Dark in color.<br />
Igneous Rhyolite Small mineral grains of quartz, feldspar, hornblende,<br />
(extrusive) and mica, or no visible grains. Light in color.<br />
Andesite Small mineral grains of feldspar, hornblende, and mica<br />
or no visible grains. Intermediate in color.<br />
Basalt Small mineral grains of feldspar, augite, and possibly<br />
olivine or no visible grains. No quartz. Dark in color.<br />
Obsidian Glassy texture. No visible grains. Volcanic glass.<br />
Fracture looks like broken glass.<br />
Pumice Frothy texture. Floats in water. Usually light in color.<br />
Sedimentary Conglomerate Coarse grained. Gravel or pebble-size grains.<br />
(detrital) Sandstone Sand-sized grains 1/16 to 2 mm.<br />
Siltstone Grains are smaller than sand but larger than clay.<br />
Shale Smallest grains. Often dark in color. Usually platy.<br />
Sedimentary Limestone Major mineral is calcite. Usually forms in oceans and<br />
(chemical or organic) lakes. Often contains fossils.<br />
Coal Forms in swampy areas. Compacted layers of organic<br />
material, mainly plant remains.<br />
Sedimentary<br />
(chemical)<br />
Rock Salt Commonly forms by the evaporation of seawater.<br />
Metamorphic Gneiss Banding due to alternate layers of different minerals,<br />
(foliated) of different colors. Parent rock often is granite.<br />
Schist Parallel arrangement of sheetlike minerals, mainly<br />
micas. Forms from different parent rocks.<br />
Phyllite Shiny or silky appearance. May look wrinkled.<br />
Common parent rocks are shale and slate.<br />
Slate Harder, denser, and shinier than shale. Common<br />
parent rock is shale.<br />
Metamorphic Marble Calcite or dolomite. Common parent rock is limestone.<br />
(nonfoliated) Soapstone Mainly of talc. Soft with greasy feel.<br />
Quartzite Hard with interlocking quartz crystals. Common<br />
parent rock is sandstone.<br />
REFERENCE HANDBOOKS 791<br />
Matt Meadows<br />
Reference Handbooks