Troels Dyhr Pedersen.indd - Solid Mechanics
Troels Dyhr Pedersen.indd - Solid Mechanics
Troels Dyhr Pedersen.indd - Solid Mechanics
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
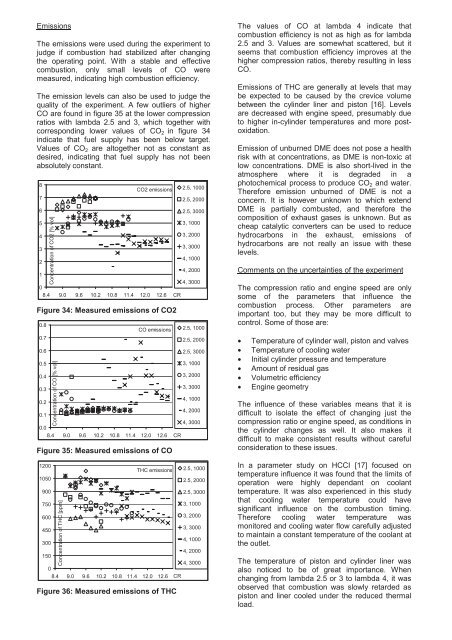
Emissions<br />
The emissions were used during the experiment to<br />
judge if combustion had stabilized after changing<br />
the operating point. With a stable and effective<br />
combustion, only small levels of CO were<br />
measured, indicating high combustion efficiency.<br />
The emission levels can also be used to judge the<br />
quality of the experiment. A few outliers of higher<br />
CO are found in figure 35 at the lower compression<br />
ratios with lambda 2.5 and 3, which together with<br />
corresponding lower values of CO2 in figure 34<br />
indicate that fuel supply has been below target.<br />
Values of CO2 are altogether not as constant as<br />
desired, indicating that fuel supply has not been<br />
absolutely constant.<br />
8<br />
7<br />
6<br />
5<br />
4<br />
3<br />
2<br />
Concentration of CO2 [% vol]<br />
CO2 emissions<br />
2.5, 1000<br />
2.5, 2000<br />
2.5, 3000<br />
3, 1000<br />
3, 2000<br />
3, 3000<br />
4, 1000<br />
4, 2000<br />
1<br />
4, 3000<br />
0<br />
8.4 9.0 9.6 10.2 10.8 11.4 12.0 12.6 CR<br />
Figure 34: Measured emissions of CO2<br />
0.8<br />
0.7<br />
0.6<br />
0.5<br />
0.4<br />
0.3<br />
0.2<br />
Concentration of CO [% vol]<br />
CO emissions<br />
2.5, 1000<br />
2.5, 2000<br />
2.5, 3000<br />
3, 1000<br />
3, 2000<br />
3, 3000<br />
4, 1000<br />
4, 2000<br />
0.1<br />
4, 3000<br />
0.0<br />
8.4 9.0 9.6 10.2 10.8 11.4 12.0 12.6 CR<br />
Figure 35: Measured emissions of CO<br />
1200<br />
1050<br />
900<br />
750<br />
600<br />
450<br />
300<br />
Concentration of THC [ppm]<br />
THC emissions<br />
2.5, 1000<br />
2.5, 2000<br />
2.5, 3000<br />
3, 1000<br />
3, 2000<br />
3, 3000<br />
4, 1000<br />
4, 2000<br />
150<br />
4, 3000<br />
0<br />
8.4 9.0 9.6 10.2 10.8 11.4 12.0 12.6 CR<br />
Figure 36: Measured emissions of THC<br />
The values of CO at lambda 4 indicate that<br />
combustion efficiency is not as high as for lambda<br />
2.5 and 3. Values are somewhat scattered, but it<br />
seems that combustion efficiency improves at the<br />
higher compression ratios, thereby resulting in less<br />
CO.<br />
Emissions of THC are generally at levels that may<br />
be expected to be caused by the crevice volume<br />
between the cylinder liner and piston [16]. Levels<br />
are decreased with engine speed, presumably due<br />
to higher in-cylinder temperatures and more postoxidation.<br />
Emission of unburned DME does not pose a health<br />
risk with at concentrations, as DME is non-toxic at<br />
low concentrations. DME is also short-lived in the<br />
atmosphere where it is degraded in a<br />
photochemical process to produce CO2 and water.<br />
Therefore emission unburned of DME is not a<br />
concern. It is however unknown to which extend<br />
DME is partially combusted, and therefore the<br />
composition of exhaust gases is unknown. But as<br />
cheap catalytic converters can be used to reduce<br />
hydrocarbons in the exhaust, emissions of<br />
hydrocarbons are not really an issue with these<br />
levels.<br />
Comments on the uncertainties of the experiment<br />
The compression ratio and engine speed are only<br />
some of the parameters that influence the<br />
combustion process. Other parameters are<br />
important too, but they may be more difficult to<br />
control. Some of those are:<br />
• Temperature of cylinder wall, piston and valves<br />
• Temperature of cooling water<br />
• Initial cylinder pressure and temperature<br />
• Amount of residual gas<br />
• Volumetric efficiency<br />
• Engine geometry<br />
The influence of these variables means that it is<br />
difficult to isolate the effect of changing just the<br />
compression ratio or engine speed, as conditions in<br />
the cylinder changes as well. It also makes it<br />
difficult to make consistent results without careful<br />
consideration to these issues.<br />
In a parameter study on HCCI [17] focused on<br />
temperature influence it was found that the limits of<br />
operation were highly dependant on coolant<br />
temperature. It was also experienced in this study<br />
that cooling water temperature could have<br />
significant influence on the combustion timing.<br />
Therefore cooling water temperature was<br />
monitored and cooling water flow carefully adjusted<br />
to maintain a constant temperature of the coolant at<br />
the outlet.<br />
The temperature of piston and cylinder liner was<br />
also noticed to be of great importance. When<br />
changing from lambda 2.5 or 3 to lambda 4, it was<br />
observed that combustion was slowly retarded as<br />
piston and liner cooled under the reduced thermal<br />
load.