Syllabus Vector Differentiation - Velocity and Acceleration - Gradient ...
Syllabus Vector Differentiation - Velocity and Acceleration - Gradient ...
Syllabus Vector Differentiation - Velocity and Acceleration - Gradient ...
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
Engineering Mathematics - II - <strong>Vector</strong> Calculus - 2007<br />
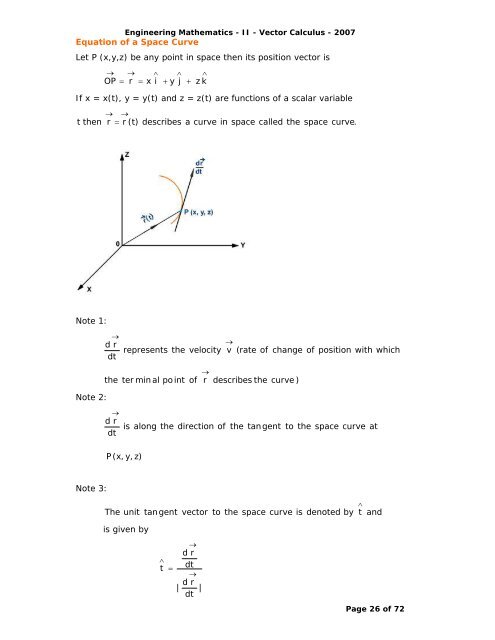
Equation of a Space Curve<br />
Let P (x,y,z) be any point in space then its position vector is<br />
<br />
OP<br />
<br />
<br />
r<br />
<br />
<br />
x i<br />
<br />
y j<br />
<br />
<br />
z k<br />
If x = x(t), y = y(t) <strong>and</strong> z = z(t) are functions of a scalar variable<br />
t then<br />
<br />
r r (t)<br />
describes<br />
a<br />
curve<br />
in<br />
space<br />
called<br />
the<br />
space<br />
curve.<br />
Note 1:<br />
<br />
d r<br />
dt<br />
represents<br />
the<br />
velocity<br />
<br />
v<br />
(rate<br />
of<br />
change<br />
of<br />
position<br />
with<br />
which<br />
the<br />
ter min al po int<br />
of<br />
<br />
r<br />
describes the<br />
curve )<br />
Note 2:<br />
<br />
d r<br />
dt<br />
is<br />
along<br />
the<br />
direction<br />
of<br />
the<br />
tan gent<br />
to<br />
the<br />
space<br />
curve<br />
at<br />
P (x, y, z)<br />
Note 3:<br />
The<br />
unit<br />
tan gent<br />
vector<br />
to<br />
the<br />
space<br />
curve<br />
is<br />
denoted by<br />
<br />
t<br />
<strong>and</strong><br />
is given by<br />
<br />
d r<br />
<br />
t <br />
dt<br />
<br />
d r<br />
| |<br />
dt<br />
Page 26 of 72