Syllabus Vector Differentiation - Velocity and Acceleration - Gradient ...
Syllabus Vector Differentiation - Velocity and Acceleration - Gradient ...
Syllabus Vector Differentiation - Velocity and Acceleration - Gradient ...
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
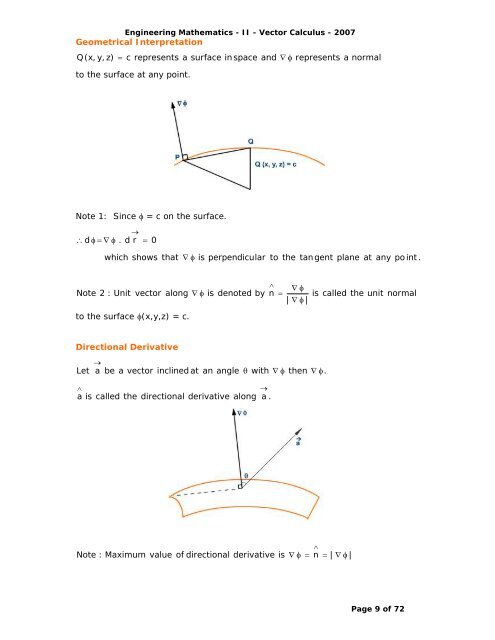
Engineering Mathematics - II - <strong>Vector</strong> Calculus - 2007<br />
Geometrical Interpretation<br />
Q(x, y, z)<br />
c represents a surface in space <strong>and</strong><br />
to the surface at any point.<br />
<br />
represents a normal<br />
Note 1: Since = c on the surface.<br />
<br />
d . d r<br />
<br />
0<br />
which<br />
shows<br />
that<br />
<br />
is<br />
perpendicular<br />
to<br />
the<br />
tan gent<br />
plane<br />
at<br />
any<br />
po int .<br />
Note<br />
2 : Unit<br />
vector<br />
along<br />
<br />
is<br />
denoted by<br />
<br />
n<br />
<br />
<br />
is<br />
| |<br />
called<br />
the<br />
unit<br />
normal<br />
to the surface (x,y,z) = c.<br />
Directional Derivative<br />
Let<br />
<br />
a<br />
be<br />
a<br />
vector<br />
inclined at<br />
an<br />
angle<br />
<br />
with<br />
<br />
then<br />
<br />
.<br />
<br />
a is<br />
called<br />
the<br />
directional<br />
derivative<br />
along<br />
<br />
a .<br />
Note : Maximum value<br />
of directional<br />
derivative<br />
is<br />
<br />
<br />
n | |<br />
Page 9 of 72