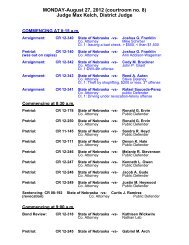
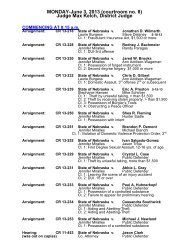
Child Support Enforcement - Sarpy County Nebraska
Child Support Enforcement - Sarpy County Nebraska
Child Support Enforcement - Sarpy County Nebraska
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
We have held that a proceeding regarding custody determinations is a special<br />
proceeding. However, we have not previously addressed whether the denial of a<br />
stay under the SCRA is an order affecting a substantial right. We find that it is.<br />
The grant of temporary custody and child support …is not a final order.<br />
Social Security<br />
(Also see Equity, Equitable Estoppel)<br />
Often times we run into situations where a parent is disabled and either seeking social<br />
security disability benefits or has qualified for the benefits. Sometimes the fact that a dependent<br />
child is receiving (or is eligible to receive) benefits through SSA becomes relevant to our court<br />
work. Below is a thumbnail primmer on the topic, as well as some relevant appellate case law.<br />
There are two types of social security benefits: Social Security Disability Insurance,<br />
SSDI and Supplemental Security Income, SSI. SSI is a needs based disability program.<br />
See generally www.ssa.gov/disability/professionals/bluebook/general-info.htm<br />
Under the Social Security disability insurance program (title II of the Act), there are three<br />
basic categories of individuals who can qualify for benefits on the basis of disability:<br />
A disabled insured worker under full retirement age.<br />
An individual disabled since childhood (before age 22) who is a dependent of a parent<br />
entitled to title II disability or retirement benefits or was a dependent of a deceased<br />
insured parent.<br />
A disabled widow or widower, age 50-60 if the deceased spouse was insured under<br />
Social Security.<br />
Under title XVI, or SSI (Supplemental Security Income), there are two basic categories<br />
under which a financially needy person can get payments based on disability:<br />
An adult age 18 or over who is disabled.<br />
A child (under age 18) who is disabled.<br />
SSI benefits are available to low income and low resource individuals, including children<br />
under age 18, who do not qualify for Social Security Disability (SSDI) benefits. The medical<br />
disability rules are the same as those for Social Security disability. Note: SSI benefits are NOT<br />
subject to income withholding/garnishment under federal law. See 5 CFR §581.104(j).<br />
Regardless of the type, social security benefits may be taxable. Tax obligations ensue<br />
when the recipient has other sources of income besides the disability benefits, or if their spouse<br />
earns a substantial income.<br />
If recipients file a federal tax return as an "individual" and report a combined income<br />
between $25,000 and $34,000, they may have to pay income tax on 50 percent of their Social<br />
Security benefits. For combined incomes above $34,000, up to 85 percent of the Social Security<br />
benefits are subject to income tax.<br />
Recipients who are married and file a joint return may have to pay taxes on 50 percent<br />
of their benefits if the recipient and his/her spouse has a combined income between $32,000<br />
and $44,000. If the combined income is more than $44,000, up to 85 percent of your Social<br />
Security benefits are subject to income tax.<br />
- 172 -