Technical Development of Waste Sector in Sweden: Survey
Technical Development of Waste Sector in Sweden: Survey
Technical Development of Waste Sector in Sweden: Survey
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
MASTER’S THESIS IN ENVIRONMENTAL STRATEGIES RESEARCH<br />
2. Environmental protection,<br />
3. Resource value <strong>of</strong> waste clos<strong>in</strong>g the loop,<br />
4. Institutional development<br />
5. Responsible issues and<br />
6. Public awareness over the time.<br />
Environmental rules and regulations are also the key drivers <strong>in</strong> technical development <strong>in</strong> the waste<br />
sector <strong>of</strong> <strong>Sweden</strong>. To achieve susta<strong>in</strong>ability goal, <strong>Sweden</strong> has started to take measure <strong>of</strong> susta<strong>in</strong>ability<br />
<strong>in</strong>dicator and put restriction on waste management system like on landfill<strong>in</strong>g. Producer’s<br />
responsibility <strong>in</strong> production and landfill tax has dramatic <strong>in</strong>fluence <strong>in</strong> reduc<strong>in</strong>g the volume <strong>of</strong> landfill<br />
waste <strong>in</strong> the waste management system <strong>of</strong> <strong>Sweden</strong>. Moreover, after <strong>in</strong>augurat<strong>in</strong>g the producers’<br />
responsibility, landfill tax and bann<strong>in</strong>g the landfill for certa<strong>in</strong> waste streams, recycl<strong>in</strong>g <strong>of</strong> materials<br />
and energy is recovered <strong>in</strong> double from 1994 to 2004 (SEPA, 2005).<br />
4.2 What does <strong>Waste</strong> Mean?<br />
Accord<strong>in</strong>g to European Union waste directive (EU Directive 2008/98/EC), “waste means any substance<br />
or object which the holder discards or <strong>in</strong>tends or is required to discard”. The transformation <strong>of</strong> a useful product<br />
<strong>in</strong>to waste strongly depends on the function it has for the owner and its economic value and as per<br />
Ludw<strong>in</strong>g et al., (2003) waste is the material with ’no economic value’’. However, the def<strong>in</strong>ition <strong>of</strong><br />
classical economic <strong>of</strong> waste may not be applicable for the traditional MSW because waste has<br />
significant resource value (Wilson, 2007) today. In traditional classification, waste is divided <strong>in</strong>to<br />
three different categories as domestic, <strong>in</strong>dustrial and hazardous waste (Hartln, 1996). The physical<br />
composition <strong>of</strong> municipal solid waste (MSW) <strong>in</strong>cludes organic and <strong>in</strong>organic waste and comb<strong>in</strong>ed<br />
with paper products, plastics, food, yard waste, textile, rubber, glass, metal, dirt, bulky waste and also<br />
different other types <strong>of</strong> waste fractions (Pichtel, 2005, p6). However, the composition <strong>of</strong> waste<br />
changes over time due to changes <strong>in</strong> the consumption pattern <strong>of</strong> the products. The categories <strong>of</strong><br />
waste have been <strong>in</strong>creas<strong>in</strong>g over time based on the sources <strong>of</strong> generation.<br />
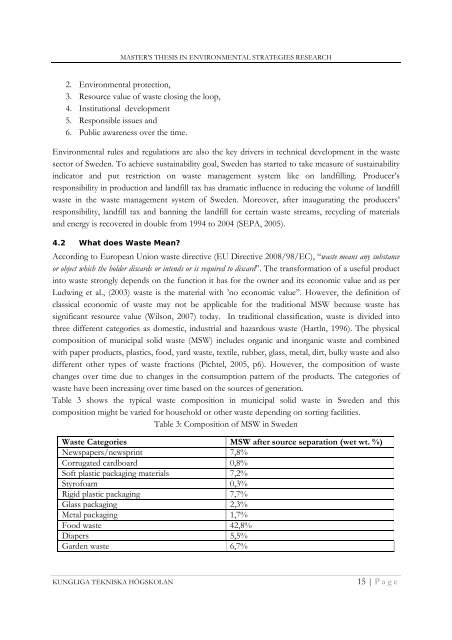
Table 3 shows the typical waste composition <strong>in</strong> municipal solid waste <strong>in</strong> <strong>Sweden</strong> and this<br />
composition might be varied for household or other waste depend<strong>in</strong>g on sort<strong>in</strong>g facilities.<br />
Table 3: Composition <strong>of</strong> MSW <strong>in</strong> <strong>Sweden</strong><br />
<strong>Waste</strong> Categories MSW after source separation (wet wt. %)<br />
Newspapers/newspr<strong>in</strong>t 7,8%<br />
Corrugated cardboard 0,8%<br />
S<strong>of</strong>t plastic packag<strong>in</strong>g materials 7,2%<br />
Styr<strong>of</strong>oam 0,3%<br />
Rigid plastic packag<strong>in</strong>g 7,7%<br />
Glass packag<strong>in</strong>g 2,3%<br />
Metal packag<strong>in</strong>g 1,7%<br />
Food waste 42,8%<br />
Diapers 5,5%<br />
Garden waste 6,7%<br />
KUNGLIGA TEKNISKA HÖGSKOLAN<br />
15 | Page