Highway Slope Manual
Highway Slope Manual
Highway Slope Manual
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
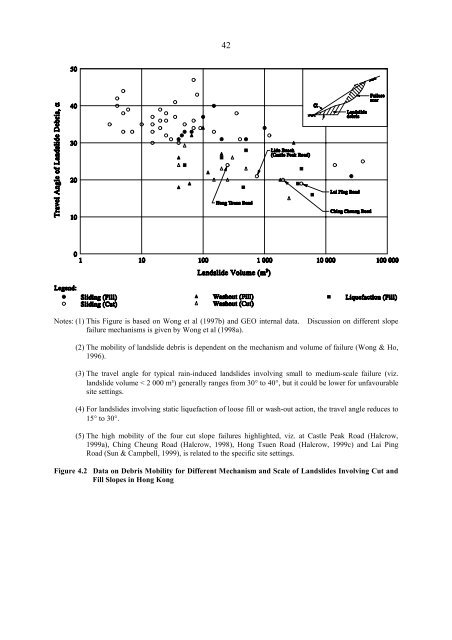
42<br />
Notes: (1) This Figure is based on Wong et al (1997b) and GEO internal data.<br />
failure mechanisms is given by Wong et al (1998a).<br />
Discussion on different slope<br />
(2) The mobility of landslide debris is dependent on the mechanism and volume of failure (Wong & Ho,<br />
1996).<br />
(3) The travel angle for typical rain-induced landslides involving small to medium-scale failure (viz.<br />
landslide volume < 2 000 m3) generally ranges from 30° to 40°, but it could be lower for unfavourable<br />
site settings.<br />
(4) For landslides involving static liquefaction of loose fill or wash-out action, the travel angle reduces to<br />
15° to 30°.<br />
(5) The high mobility of the four cut slope failures highlighted, viz. at Castle Peak Road (Halcrow,<br />
1999a), Ching Cheung Road (Halcrow, 1998), Hong Tsuen Road (Halcrow, 1999c) and Lai Ping<br />
Road (Sun & Campbell, 1999), is related to the specific site settings.<br />
Figure 4.2 Data on Debris Mobility for Different Mechanism and Scale of Landslides Involving Cut and<br />
Fill <strong>Slope</strong>s in Hong Kong