Highway Slope Manual
Highway Slope Manual
Highway Slope Manual
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
66<br />
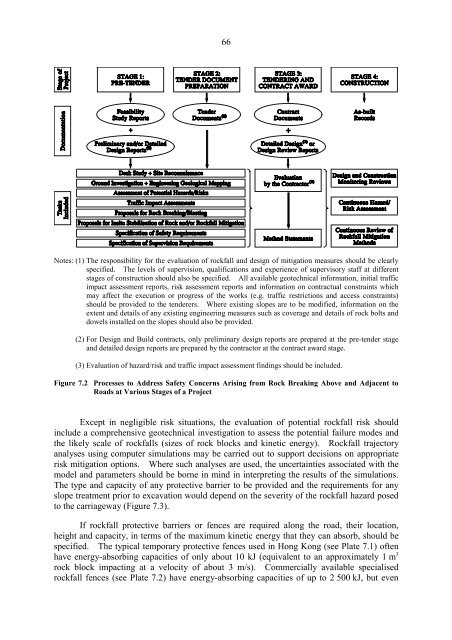
Notes: (1) The responsibility for the evaluation of rockfall and design of mitigation measures should be clearly<br />
specified. The levels of supervision, qualifications and experience of supervisory staff at different<br />
stages of construction should also be specified. All available geotechnical information, initial traffic<br />
impact assessment reports, risk assessment reports and information on contractual constraints which<br />
may affect the execution or progress of the works (e.g. traffic restrictions and access constraints)<br />
should be provided to the tenderers. Where existing slopes are to be modified, information on the<br />
extent and details of any existing engineering measures such as coverage and details of rock bolts and<br />
dowels installed on the slopes should also be provided.<br />
(2) For Design and Build contracts, only preliminary design reports are prepared at the pre 叫 tender stage<br />
and detailed design reports are prepared by the contractor at the contract award stage.<br />
(3) Evaluation of hazard/risk and traffic impact assessment findings should be included.<br />
Figure 7.2 Processes to Address Safety Concerns Arising from Rock Breaking Above and Adiacent to<br />
Roads at Various Stages of a Proiect<br />
Except in negligible risk situations, the evaluation of potential rockfall risk should<br />
include a comprehensive geotechnical investigation to assess the potential failure modes and<br />
the likely scale of rockfalls (sizes of rock blocks and kinetic energy). Rockfall trajectory<br />
analyses using computer simulations may be carried out to support decisions on appropriate<br />
risk mitigation options. Where such analyses are used, the uncertainties associated with the<br />
model and parameters should be borne in mind in interpreting the results of the simulations.<br />
The type and capacity of any protective barrier to be provided and the requirements for any<br />
slope treatment prior to excavation would depend on the severity of the rockfall hazard posed<br />
to the carriageway (Figure 7.3).<br />
If rockfall protective barriers or fences are required along the road, their location,<br />
height and capacity, in terms of the maximum kinetic energy that they can absorb, should be<br />
specified. The typical temporary protective fences used in Hong Kong (see Plate 7.1) often<br />
have energy-absorbing capacities of only about 10 kJ (equivalent to an approximately 1 m 3<br />
rock block impacting at a velocity of about 3 m/s). Commercially available specialised<br />
rockfall fences (see Plate 7.2) have energy-absorbing capacities of up to 2 500 kJ, but even