6th International Workshop on Breast Densitometry and Breast ...
6th International Workshop on Breast Densitometry and Breast ...
6th International Workshop on Breast Densitometry and Breast ...
- No tags were found...
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
6 th <str<strong>on</strong>g>Internati<strong>on</strong>al</str<strong>on</strong>g> <str<strong>on</strong>g>Workshop</str<strong>on</strong>g> <strong>on</strong> <strong>Breast</strong> <strong>Densitometry</strong><br />
<strong>and</strong> <strong>Breast</strong> Cancer Risk Assessment<br />
P3 COMPARISON OF CUMULUS AREA DENSITY WITH TWO AUTOMATED<br />
VOLUMETRIC BREAST DENSITY ALGORITHMS<br />
Olivier Al<strong>on</strong>zo-Proulx 1 , Martin Yaffe 1 , Jennifer Harvey 2 .<br />
1 Sunnybrook Health Sciences Centre, 2075 Bayview Ave., Tor<strong>on</strong>to, Ontario Canada, M4N 3M5;<br />
2 University of Virginia Health System, Charlottesville, Virginia<br />
Purpose: Measurements of breast density made with the Cumulus interactive threshold algorithm have<br />
been shown to be moderately associated with breast cancer risk. In this work we compare two volumetric<br />
density (VBD) measures (the volume proporti<strong>on</strong> of fibrogl<strong>and</strong>ular tissue), with Cumulus area percent<br />
density (PD) to validate the volumetric algorithms.<br />
ABSTRACTS<br />
Methods <strong>and</strong> materials: 310 women who had both film-screen (FS) <strong>and</strong> digital mammograms as part of<br />
the ACRIN DMIST were analyzed for PD (left CC, FS) <strong>and</strong> VBD (left <strong>and</strong> right CC, digital). One VBD<br />
algorithm, ‘Cumulus Volume’ is based <strong>on</strong> a prior calibrati<strong>on</strong> of the imaging signal versus tissue thickness<br />
<strong>and</strong> compositi<strong>on</strong>. The sec<strong>on</strong>d algorithm, ‘Volpara’, finds a pixel where <strong>on</strong>ly fatty tissue is present, whose<br />
signal intensity is then used as a reference to determine the density <strong>on</strong> the image. PD <strong>and</strong> both VBD<br />
values were compared, <strong>and</strong> density color maps were visually reviewed. The relati<strong>on</strong> between the VBD of<br />
the left-right pairs was investigated, as well as the relati<strong>on</strong> between the two volumetric algorithms.<br />
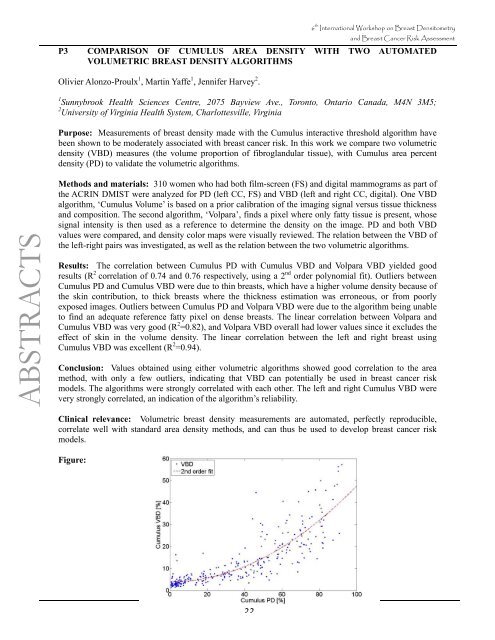
Results: The correlati<strong>on</strong> between Cumulus PD with Cumulus VBD <strong>and</strong> Volpara VBD yielded good<br />
results (R 2 correlati<strong>on</strong> of 0.74 <strong>and</strong> 0.76 respectively, using a 2 nd order polynomial fit). Outliers between<br />
Cumulus PD <strong>and</strong> Cumulus VBD were due to thin breasts, which have a higher volume density because of<br />
the skin c<strong>on</strong>tributi<strong>on</strong>, to thick breasts where the thickness estimati<strong>on</strong> was err<strong>on</strong>eous, or from poorly<br />
exposed images. Outliers between Cumulus PD <strong>and</strong> Volpara VBD were due to the algorithm being unable<br />
to find an adequate reference fatty pixel <strong>on</strong> dense breasts. The linear correlati<strong>on</strong> between Volpara <strong>and</strong><br />
Cumulus VBD was very good (R 2 =0.82), <strong>and</strong> Volpara VBD overall had lower values since it excludes the<br />
effect of skin in the volume density. The linear correlati<strong>on</strong> between the left <strong>and</strong> right breast using<br />
Cumulus VBD was excellent (R 2 =0.94).<br />
C<strong>on</strong>clusi<strong>on</strong>: Values obtained using either volumetric algorithms showed good correlati<strong>on</strong> to the area<br />
method, with <strong>on</strong>ly a few outliers, indicating that VBD can potentially be used in breast cancer risk<br />
models. The algorithms were str<strong>on</strong>gly correlated with each other. The left <strong>and</strong> right Cumulus VBD were<br />
very str<strong>on</strong>gly correlated, an indicati<strong>on</strong> of the algorithm’s reliability.<br />
Clinical relevance: Volumetric breast density measurements are automated, perfectly reproducible,<br />
correlate well with st<strong>and</strong>ard area density methods, <strong>and</strong> can thus be used to develop breast cancer risk<br />
models.<br />
Figure:<br />
33