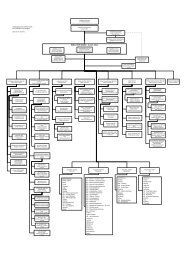
Annual Report 2010 - ProCredit Bank
Annual Report 2010 - ProCredit Bank
Annual Report 2010 - ProCredit Bank
- No tags were found...
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
70<br />
<strong>Annual</strong> <strong>Report</strong> <strong>2010</strong><br />
Influence to Economic Value of the Capital<br />
2% increase of interest rates 2% decrease of interest rates<br />
Total EUR RSD Total EUR RSD<br />
31. December <strong>2010</strong> 2009 (270,825) (259,901) (186,510) (174,130) (88,352) (90,109) 259,901 270,825 186,510 174,130 88,352 90,109<br />
Influence to Economic Value of the Capital<br />
2% increase of interest rates 2% decrease of interest rates<br />
Total EUR RSD Total EUR RSD<br />
31. December 2009 2008 (259,901) 256,780 (174,130) 320,029 (73,274) (88,352) (256,780) 259,901 (320,029) 174,130 73,274 88,352<br />
Having in mind presented volume of potential impact of the changes<br />
in interest rates to the economic capital value and profit/loss,<br />
the Group considers its interest rate risk profile to be adequate.<br />
D) Liquidity risk<br />
Liquidity risk arises in the general funding of the Group’s activities<br />
and in the management of its liquidity position. It includes both the<br />
risk of being unable to fund assets at appropriate maturities and<br />
rates and the risk of being unable to liquidate an asset at a reasonable<br />
price and in an appropriate time frame.<br />
The Group has diversified funding base. Funding base includes:<br />
• customer deposits with wide ranges of maturity<br />
• money market deposits<br />
• loans from foreign banks and financial institutions<br />
• subordinated debt<br />
• share capital<br />
The Group continually assesses liquidity risk by identifying and<br />
monitoring changes in funding required meeting business goals<br />
and targets set in terms of the overall Group’s strategy.<br />
The maturities of assets and liabilities and the ability to replace,<br />
at an acceptable cost, interest-bearing liabilities as they mature,<br />
are important factors in assessing the liquidity of the Group and its<br />
exposure to changes in interest rates and exchange rates.<br />
Monitoring and reporting take the form of cash flow measurement<br />
and projections for the next day, week and month respectively, as<br />
these are key periods for liquidity management. The starting point<br />
for those projections is an analysis of the contractual maturity of<br />
the financial liabilities and the expected collection date of the financial<br />
assets.<br />
Liquidity requirements to support calls under guarantees and<br />
standby letters of credit are considerably less than the amount of<br />
the commitment because the Group does not generally expect the<br />
third party to draw funds under the agreement. The total outstanding<br />
contractual amount of commitments to extend credit does not<br />
necessarily represents future cash requirements, since many of<br />
these commitments will expire or terminate without being funded.<br />
D.1 Non derivatives cash flow<br />
The table below presents the cash flows payable by the Group under<br />
non-derivative financial liabilities by remaining contractual<br />
maturities at the balance sheet date. The amounts disclosed in the<br />
table are the contractual undiscounted cash flows, whereas the<br />
Group manages the inherent liquidity risk based on expected undiscounted<br />
cash inflows.<br />
As at 31 December <strong>2010</strong> Up to 1 – 3 3 –6 6 – 12 1 – 4 Over Total<br />
1 month months months months years 4 years<br />
Financial Liabilities<br />
Liabilities to banks 2,215,022 – – – – – 2,215,022<br />
Due to customers 8,423,786 11,384,001 8,249,774 7,516,066 1,421,301 251,890 37,246,818<br />
Other borrowed funds 1,279,205 587,495 574,464 2,366,592 15,001,577 1,820,481 21,629,813<br />
Provisions 4,964 9,927 14,891 29,781 – 32,670 92,233<br />
Subordinated debt 6,578 134,246 13,131 129,557 1,420,736 1,815,600 3,519,848<br />
Other liabilities 77,425 – 1,916 – – – 79,341<br />
Total Financial Liabilities<br />
(by contractual due dates) 12,006,980 12,115,669 8,854,176 9,104,222 18,546,865 4,155,163 64,783,075<br />
Total Financial Assets<br />
(by expected due dates) 23,540,235 4,549,756 6,266,205 10,400,006 26,383,870 6,513,465 77,653,537<br />
As at 31 December 2009 Up to 1 – 3 3 – 12 1 – 2 2 – 5 Over Total<br />
1 month months months years years 5 years<br />
Financial Liabilities<br />
Liabilities to banks 354,261 – – – – – 354,261<br />
Due to customers 19,960,440 6,297,730 10,734,569 905,071 583,167 138,068 38,619,045<br />
Other borrowed funds 1,486,875 554,265 2,770,244 4,244,732 9,322,058 565,331 18,943,505<br />
Provisions 2,078 23,052 11,989 – – 37,581 74,700<br />
Subordinated debt 2,743 77,959 136,571 221,946 2,942,580 – 3,381,799<br />
Other liabilities 110,908 100,651 – – – – 211,559<br />
Total Financial Liabilities<br />
(by contractual due dates) 21,917,305 7,053,657 13,653,373 5,371,749 12,847,805 740,980 61,584,869<br />
Total Financial Assets<br />
(by expected due dates) 20,452,629 3,564,894 13,811,677 9,776,202 15,347,164 4,065,472 67,018,038