Cost-Based Optimization of Integration Flows - Datenbanken ...
Cost-Based Optimization of Integration Flows - Datenbanken ...
Cost-Based Optimization of Integration Flows - Datenbanken ...
- No tags were found...
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
3.5 Experimental Evaluation<br />
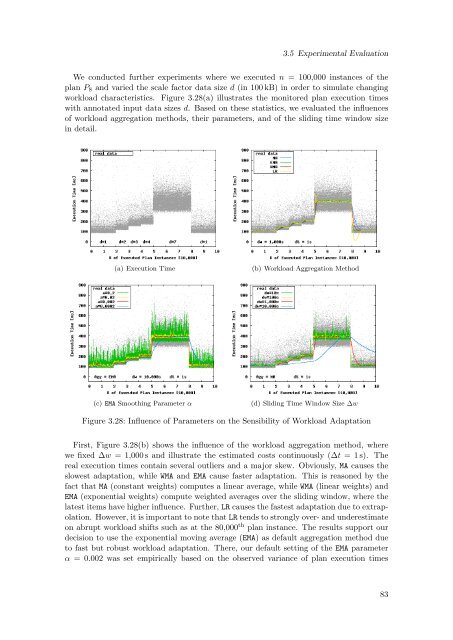
We conducted further experiments where we executed n = 100,000 instances <strong>of</strong> the<br />
plan P 8 and varied the scale factor data size d (in 100 kB) in order to simulate changing<br />
workload characteristics. Figure 3.28(a) illustrates the monitored plan execution times<br />
with annotated input data sizes d. <strong>Based</strong> on these statistics, we evaluated the influences<br />
<strong>of</strong> workload aggregation methods, their parameters, and <strong>of</strong> the sliding time window size<br />
in detail.<br />
(a) Execution Time<br />
(b) Workload Aggregation Method<br />
(c) EMA Smoothing Parameter α<br />
(d) Sliding Time Window Size ∆w<br />
Figure 3.28: Influence <strong>of</strong> Parameters on the Sensibility <strong>of</strong> Workload Adaptation<br />
First, Figure 3.28(b) shows the influence <strong>of</strong> the workload aggregation method, where<br />
we fixed ∆w = 1,000 s and illustrate the estimated costs continuously (∆t = 1 s). The<br />
real execution times contain several outliers and a major skew. Obviously, MA causes the<br />
slowest adaptation, while WMA and EMA cause faster adaptation. This is reasoned by the<br />
fact that MA (constant weights) computes a linear average, while WMA (linear weights) and<br />
EMA (exponential weights) compute weighted averages over the sliding window, where the<br />
latest items have higher influence. Further, LR causes the fastest adaptation due to extrapolation.<br />
However, it is important to note that LR tends to strongly over- and underestimate<br />
on abrupt workload shifts such as at the 80,000 th plan instance. The results support our<br />
decision to use the exponential moving average (EMA) as default aggregation method due<br />
to fast but robust workload adaptation. There, our default setting <strong>of</strong> the EMA parameter<br />
α = 0.002 was set empirically based on the observed variance <strong>of</strong> plan execution times<br />
83