Download (2461kB) - University of Greenwich
Download (2461kB) - University of Greenwich
Download (2461kB) - University of Greenwich
- No tags were found...
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
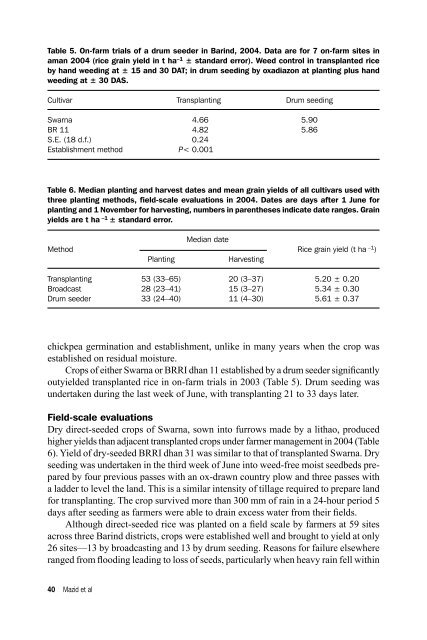
Table 5. On-farm trials <strong>of</strong> a drum seeder in Barind, 2004. Data are for 7 on-farm sites inaman 2004 (rice grain yield in t ha –1 ± standard error). Weed control in transplanted riceby hand weeding at ± 15 and 30 DAT; in drum seeding by oxadiazon at planting plus handweeding at ± 30 DAS.Cultivar Transplanting Drum seedingSwarna 4.66 5.90BR 11 4.82 5.86S.E. (18 d.f.) 0.24Establishment method P< 0.001Table 6. Median planting and harvest dates and mean grain yields <strong>of</strong> all cultivars used withthree planting methods, field-scale evaluations in 2004. Dates are days after 1 June forplanting and 1 November for harvesting, numbers in parentheses indicate date ranges. Grainyields are t ha –1 ± standard error.Median dateMethod Rice grain yield (t ha –1 )PlantingHarvestingTransplanting 53 (33–65) 20 (3–37) 5.20 ± 0.20Broadcast 28 (23–41) 15 (3–27) 5.34 ± 0.30Drum seeder 33 (24–40) 11 (4–30) 5.61 ± 0.37chickpea germination and establishment, unlike in many years when the crop wasestablished on residual moisture.Crops <strong>of</strong> either Swarna or BRRI dhan 11 established by a drum seeder significantlyoutyielded transplanted rice in on-farm trials in 2003 (Table 5). Drum seeding wasundertaken during the last week <strong>of</strong> June, with transplanting 21 to 33 days later.Field-scale evaluationsDry direct-seeded crops <strong>of</strong> Swarna, sown into furrows made by a lithao, producedhigher yields than adjacent transplanted crops under farmer management in 2004 (Table6). Yield <strong>of</strong> dry-seeded BRRI dhan 31 was similar to that <strong>of</strong> transplanted Swarna. Dryseeding was undertaken in the third week <strong>of</strong> June into weed-free moist seedbeds preparedby four previous passes with an ox-drawn country plow and three passes witha ladder to level the land. This is a similar intensity <strong>of</strong> tillage required to prepare landfor transplanting. The crop survived more than 300 mm <strong>of</strong> rain in a 24-hour period 5days after seeding as farmers were able to drain excess water from their fields.Although direct-seeded rice was planted on a field scale by farmers at 59 sitesacross three Barind districts, crops were established well and brought to yield at only26 sites—13 by broadcasting and 13 by drum seeding. Reasons for failure elsewhereranged from flooding leading to loss <strong>of</strong> seeds, particularly when heavy rain fell within40 Mazid et al