Managing Risks of Supply-Chain Disruptions: Dual ... - CiteSeerX
Managing Risks of Supply-Chain Disruptions: Dual ... - CiteSeerX
Managing Risks of Supply-Chain Disruptions: Dual ... - CiteSeerX
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
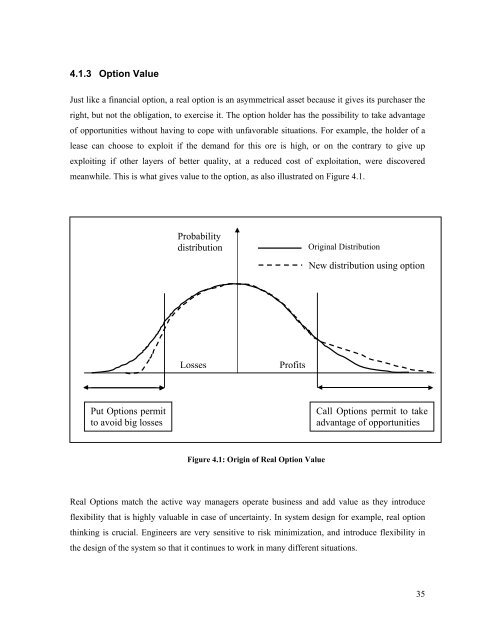
4.1.3 Option ValueJust like a financial option, a real option is an asymmetrical asset because it gives its purchaser theright, but not the obligation, to exercise it. The option holder has the possibility to take advantage<strong>of</strong> opportunities without having to cope with unfavorable situations. For example, the holder <strong>of</strong> alease can choose to exploit if the demand for this ore is high, or on the contrary to give upexploiting if other layers <strong>of</strong> better quality, at a reduced cost <strong>of</strong> exploitation, were discoveredmeanwhile. This is what gives value to the option, as also illustrated on Figure 4.1.ProbabilitydistributionOriginal DistributionNew distribution using optionLossesPr<strong>of</strong>itsPut Options permitto avoid big lossesCall Options permit to takeadvantage <strong>of</strong> opportunitiesFigure 4.1: Origin <strong>of</strong> Real Option ValueReal Options match the active way managers operate business and add value as they introduceflexibility that is highly valuable in case <strong>of</strong> uncertainty. In system design for example, real optionthinking is crucial. Engineers are very sensitive to risk minimization, and introduce flexibility inthe design <strong>of</strong> the system so that it continues to work in many different situations.35