Managing Risks of Supply-Chain Disruptions: Dual ... - CiteSeerX
Managing Risks of Supply-Chain Disruptions: Dual ... - CiteSeerX
Managing Risks of Supply-Chain Disruptions: Dual ... - CiteSeerX
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
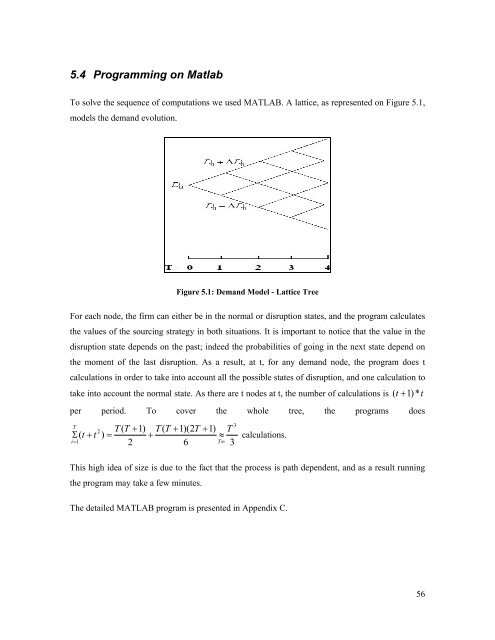
5.4 Programming on MatlabTo solve the sequence <strong>of</strong> computations we used MATLAB. A lattice, as represented on Figure 5.1,models the demand evolution.Figure 5.1: Demand Model - Lattice TreeFor each node, the firm can either be in the normal or disruption states, and the program calculatesthe values <strong>of</strong> the sourcing strategy in both situations. It is important to notice that the value in thedisruption state depends on the past; indeed the probabilities <strong>of</strong> going in the next state depend onthe moment <strong>of</strong> the last disruption. As a result, at t, for any demand node, the program does tcalculations in order to take into account all the possible states <strong>of</strong> disruption, and one calculation totake into account the normal state. As there are t nodes at t, the number <strong>of</strong> calculations is( t + 1) *per period. To cover the whole tree, the programs doesT32 T ( T + 1) T ( T + 1)(2T+ 1) TΣ ( t + t ) = +≈ calculations.i=126T∞3This high idea <strong>of</strong> size is due to the fact that the process is path dependent, and as a result runningthe program may take a few minutes.The detailed MATLAB program is presented in Appendix C.t56