buletin Åtiin ific - Facultatea de Stiinte Economice - Universitatea din ...
buletin Åtiin ific - Facultatea de Stiinte Economice - Universitatea din ...
buletin Åtiin ific - Facultatea de Stiinte Economice - Universitatea din ...
- No tags were found...
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
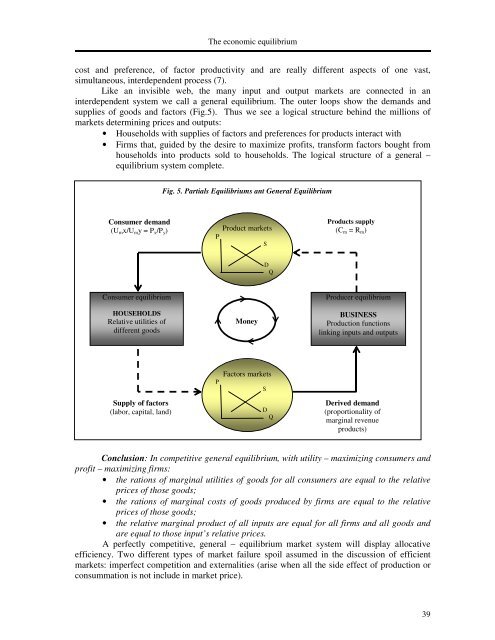
The economic equilibriumcost and preference, of factor productivity and are really different aspects of one vast,simultaneous, inter<strong>de</strong>pen<strong>de</strong>nt process (7).Like an invisible web, the many input and output markets are connected in aninter<strong>de</strong>pen<strong>de</strong>nt system we call a general equilibrium. The outer loops show the <strong>de</strong>mands andsupplies of goods and factors (Fig.5). Thus we see a logical structure behind the millions ofmarkets <strong>de</strong>termining prices and outputs:• Households with supplies of factors and preferences for products interact with• Firms that, gui<strong>de</strong>d by the <strong>de</strong>sire to maximize profits, transform factors bought fromhouseholds into products sold to households. The logical structure of a general –equilibrium system complete.Fig. 5. Partials Equilibriums ant General EquilibriumConsumer <strong>de</strong>mand(U m x/U m y = P x /P y )Product marketsPSProducts supply(C m = R m )DQConsumer equilibriumHOUSEHOLDSRelative utilities ofdifferent goodsMoneyProducer equilibriumBUSINESSProduction functionslinking inputs and outputsPFactors marketsSSupply of factors(labor, capital, land)DQDerived <strong>de</strong>mand(proportionality ofmarginal revenueproducts)Conclusion: In competitive general equilibrium, with utility – maximizing consumers andprofit – maximizing firms:• the rations of marginal utilities of goods for all consumers are equal to the relativeprices of those goods;• the rations of marginal costs of goods produced by firms are equal to the relativeprices of those goods;• the relative marginal product of all inputs are equal for all firms and all goods andare equal to those input’s relative prices.A perfectly competitive, general – equilibrium market system will display allocativeefficiency. Two different types of market failure spoil assumed in the discussion of efficientmarkets: imperfect competition and externalities (arise when all the si<strong>de</strong> effect of production orconsummation is not inclu<strong>de</strong> in market price).39