2011 - Division of Administration - Louisiana
2011 - Division of Administration - Louisiana
2011 - Division of Administration - Louisiana
- No tags were found...
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
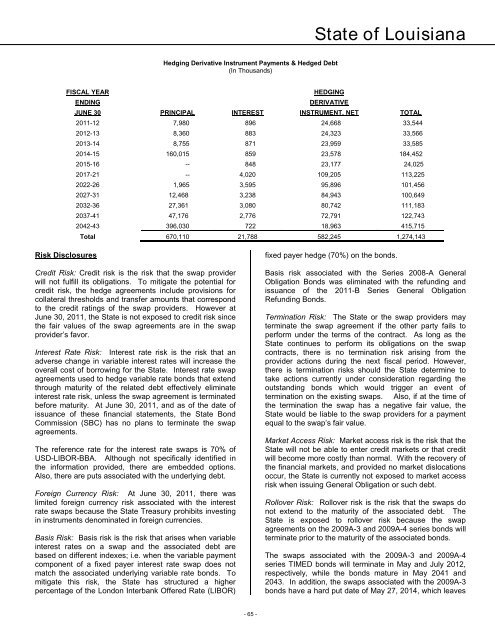
State <strong>of</strong> <strong>Louisiana</strong>Hedging Derivative Instrument Payments & Hedged Debt(In Thousands)FISCAL YEARHEDGINGENDINGDERIVATIVEJUNE 30 PRINCIPAL INTEREST INSTRUMENT, NET TOTAL<strong>2011</strong>-12 7,980 896 24,668 33,5442012-13 8,360 883 24,323 33,5662013-14 8,755 871 23,959 33,5852014-15 160,015 859 23,578 184,4522015-16 -- 848 23,177 24,0252017-21 -- 4,020 109,205 113,2252022-26 1,965 3,595 95,896 101,4562027-31 12,468 3,238 84,943 100,6492032-36 27,361 3,080 80,742 111,1832037-41 47,176 2,776 72,791 122,7432042-43 396,030 722 18,963 415,715Total 670,110 21,788 582,245 1,274,143Risk DisclosuresCredit Risk: Credit risk is the risk that the swap providerwill not fulfill its obligations. To mitigate the potential forcredit risk, the hedge agreements include provisions forcollateral thresholds and transfer amounts that correspondto the credit ratings <strong>of</strong> the swap providers. However atJune 30, <strong>2011</strong>, the State is not exposed to credit risk sincethe fair values <strong>of</strong> the swap agreements are in the swapprovider’s favor.Interest Rate Risk: Interest rate risk is the risk that anadverse change in variable interest rates will increase theoverall cost <strong>of</strong> borrowing for the State. Interest rate swapagreements used to hedge variable rate bonds that extendthrough maturity <strong>of</strong> the related debt effectively eliminateinterest rate risk, unless the swap agreement is terminatedbefore maturity. At June 30, <strong>2011</strong>, and as <strong>of</strong> the date <strong>of</strong>issuance <strong>of</strong> these financial statements, the State BondCommission (SBC) has no plans to terminate the swapagreements.The reference rate for the interest rate swaps is 70% <strong>of</strong>USD-LIBOR-BBA. Although not specifically identified inthe information provided, there are embedded options.Also, there are puts associated with the underlying debt.Foreign Currency Risk: At June 30, <strong>2011</strong>, there waslimited foreign currency risk associated with the interestrate swaps because the State Treasury prohibits investingin instruments denominated in foreign currencies.Basis Risk: Basis risk is the risk that arises when variableinterest rates on a swap and the associated debt arebased on different indexes; i.e. when the variable paymentcomponent <strong>of</strong> a fixed payer interest rate swap does notmatch the associated underlying variable rate bonds. Tomitigate this risk, the State has structured a higherpercentage <strong>of</strong> the London Interbank Offered Rate (LIBOR)fixed payer hedge (70%) on the bonds.Basis risk associated with the Series 2008-A GeneralObligation Bonds was eliminated with the refunding andissuance <strong>of</strong> the <strong>2011</strong>-B Series General ObligationRefunding Bonds.Termination Risk: The State or the swap providers mayterminate the swap agreement if the other party fails toperform under the terms <strong>of</strong> the contract. As long as theState continues to perform its obligations on the swapcontracts, there is no termination risk arising from theprovider actions during the next fiscal period. However,there is termination risks should the State determine totake actions currently under consideration regarding theoutstanding bonds which would trigger an event <strong>of</strong>termination on the existing swaps. Also, if at the time <strong>of</strong>the termination the swap has a negative fair value, theState would be liable to the swap providers for a paymentequal to the swap’s fair value.Market Access Risk: Market access risk is the risk that theState will not be able to enter credit markets or that creditwill become more costly than normal. With the recovery <strong>of</strong>the financial markets, and provided no market dislocationsoccur, the State is currently not exposed to market accessrisk when issuing General Obligation or such debt.Rollover Risk: Rollover risk is the risk that the swaps donot extend to the maturity <strong>of</strong> the associated debt. TheState is exposed to rollover risk because the swapagreements on the 2009A-3 and 2009A-4 series bonds willterminate prior to the maturity <strong>of</strong> the associated bonds.The swaps associated with the 2009A-3 and 2009A-4series TIMED bonds will terminate in May and July 2012,respectively, while the bonds mature in May 2041 and2043. In addition, the swaps associated with the 2009A-3bonds have a hard put date <strong>of</strong> May 27, 2014, which leaves- 65 -