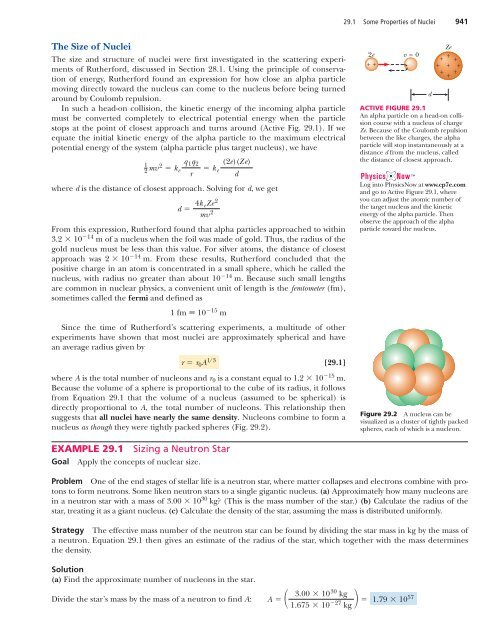
29.1 Some Properties of Nuclei 941The Size of NucleiThe size and structure of nuclei were first investigated in the scattering experimentsof Rutherford, discussed in Section 28.1. Using the principle of conservationof energy, Rutherford found an expression for how close an alpha particlemoving directly toward the nucleus can come to the nucleus before being turnedaround by Coulomb repulsion.In such a head-on collision, the kinetic energy of the incoming alpha particlemust be converted completely to electrical potential energy when the particlestops at the point of closest approach and turns around (Active Fig. 29.1). If weequate the initial kinetic energy of the alpha particle to the maximum electricalpotential energy of the system (alpha particle plus target nucleus), we have12 mv 2 q 1 q 2 k erwhere d is the distance of closest approach. Solving for d, we getd 4k eZe 2mv 2From this expression, Rutherford found that alpha particles approached to within3.2 10 14 m of a nucleus when the foil was made of gold. Thus, the radius of thegold nucleus must be less than this value. For silver atoms, the distance of closestapproach was 2 10 14 m. From these results, Rutherford concluded that thepositive charge in an atom is concentrated in a small sphere, which he called thenucleus, with radius no greater than about 10 14 m. Because such small lengthsare common in nuclear physics, a convenient unit of length is the femtometer (fm),sometimes called the fermi and defined as1 fm 10 15 mSince the time of Rutherford’s scattering experiments, a multitude of otherexperiments have shown that most nuclei are approximately spherical and havean average radius given byr r 0 A 1/3 k e(2e)(Ze)d[29.1]where A is the total number of nucleons and r 0 is a constant equal to 1.2 10 15 m.Because the volume of a sphere is proportional to the cube of its radius, it followsfrom Equation 29.1 that the volume of a nucleus (assumed to be spherical) isdirectly proportional to A, the total number of nucleons. This relationship thensuggests that all nuclei have nearly the same density. Nucleons combine to form anucleus as though they were tightly packed spheres (Fig. 29.2).Ze2e v = 0++ +++ ++ ++ ++ACTIVE FIGURE 29.1An alpha particle on a head-on collisioncourse with a nucleus of chargeZe. Because of the Coulomb repulsionbetween the like charges, the alphaparticle will stop instantaneously at adistance d from the nucleus, calledthe distance of closest approach.Log into <strong>Physics</strong>Now at www.cp7e.comand go to Active Figure 29.1, whereyou can adjust the atomic number ofthe target nucleus and the kineticenergy of the alpha particle. Thenobserve the approach of the alphaparticle toward the nucleus.Figure 29.2 A nucleus can bevisualized as a cluster of tightly packedspheres, each of which is a nucleon.dEXAMPLE 29.1GoalSizing a Neutron StarApply the concepts of nuclear size.Problem One of the end stages of stellar life is a neutron star, where matter collapses and electrons combine with protonsto form neutrons. Some liken neutron stars to a single gigantic nucleus. (a) Approximately how many nucleons arein a neutron star with a mass of 3.00 10 30 kg? (This is the mass number of the star.) (b) Calculate the radius of thestar, treating it as a giant nucleus. (c) Calculate the density of the star, assuming the mass is distributed uniformly.Strategy The effective mass number of the neutron star can be found by dividing the star mass in kg by the mass ofa neutron. Equation 29.1 then gives an estimate of the radius of the star, which together with the mass determinesthe density.Solution(a) Find the approximate number of nucleons in the star.Divide the star’s mass by the mass of a neutron to find A: 1.79 10 57A 3.00 10 30 kg1.675 10 27 kg
942 Chapter 29 Nuclear <strong>Physics</strong>(b) Calculate the radius of the star, treating it as a giantatomic nucleus.Substitute into Equation 29.1: r r 0 A 1/3 (1.2 10 15 m)(1.79 10 57 ) 1/3 1.46 10 4 m(c) Calculate the density of the star, assuming that itsmass is distributed uniformly.Substitute values into the equation for density andassume the star is a uniform sphere: m V m43r 3 3.00 1030 kg43 (1.46 10 4 m) 3 2.30 10 17 kg/m 3Remarks This density is typical of atomic nuclei as well as of neutron stars. A ball of neutron star matter having aradius of only 1 meter would have a powerful gravity field: it could attract objects a kilometer away at an accelerationof over 50 m/s 2 !Exercise 29.1Estimate the radius of a uranium-235 nucleus.Answer7.41 10 15 mMARIA GOEPPERT-MAYER,German Physicist (1906 – 1972)Goeppert-Mayer was born and educatedin Germany. She is best known for herdevelopment of the shell model of thenucleus, published in 1950. A similarmodel was simultaneously developed byHans Jensen, a German scientist. MariaGoeppert-Mayer and Hans Jensen wereawarded the Nobel Prize in physics in 1963for their extraordinary work inunderstanding the structure of the nucleus.Courtesy of Louise Barker/AIP Niels Bohr LibraryNuclear StabilityGiven that the nucleus consists of a closely packed collection of protons andneutrons, you might be surprised that it can even exist. The very large repulsiveelectrostatic forces between protons should cause the nucleus to fly apart.However, nuclei are stable because of the presence of another, short-range(about 2 fm) force: the nuclear force, an attractive force that acts between allnuclear particles. The protons attract each other via the nuclear force, and at thesame time they repel each other through the Coulomb force. The attractivenuclear force also acts between pairs of neutrons and between neutrons andprotons.The nuclear attractive force is stronger than the Coulomb repulsive forcewithin the nucleus (at short ranges). If this were not the case, stable nucleiwould not exist. Moreover, the strong nuclear force is nearly independent ofcharge. In other words, the nuclear forces associated with proton–proton,proton–neutron, and neutron–neutron interactions are approximately thesame, apart from the additional repulsive Coulomb force for the proton–protoninteraction.There are about 260 stable nuclei; hundreds of others have been observed,but are unstable. A plot of N versus Z for a number of stable nuclei is given inFigure 29.3. Note that light nuclei are most stable if they contain equal numbers ofprotons and neutrons, so that N Z, but heavy nuclei are more stable if N Z.This difference can be partially understood by recognizing that as the number ofprotons increases, the strength of the Coulomb force increases, which tends tobreak the nucleus apart. As a result, more neutrons are needed to keep thenucleus stable, because neutrons are affected only by the attractive nuclearforces. In effect, the additional neutrons “dilute” the nuclear charge density. Eventually,when Z 83, the repulsive forces between protons cannot be compensatedfor by the addition of neutrons. Elements that contain more than 83 protons don’thave stable nuclei, but decay or disintegrate into other particles in variousamounts of time. The masses and some other properties of selected isotopes areprovided in Appendix B.
- Page 1 and 2:
Color-enhanced scanning electronmic
- Page 3:
876 Chapter 27 Quantum PhysicsSolve
- Page 6 and 7:
27.2 The Photoelectric Effect and t
- Page 8 and 9:
27.3 X-Rays 881even when black card
- Page 10 and 11:
27.4 Diffraction of X-Rays by Cryst
- Page 12 and 13:
27.5 The Compton Effect 885Exercise
- Page 14 and 15:
27.6 The Dual Nature of Light and M
- Page 16 and 17:
27.6 The Dual Nature of Light and M
- Page 18 and 19: 27.8 The Uncertainty Principle 891w
- Page 20 and 21: 27.8 The Uncertainty Principle 893E
- Page 22 and 23: 27.9 The Scanning Tunneling Microsc
- Page 24 and 25: Problems 897The probability per uni
- Page 26 and 27: Problems 89917. When light of wavel
- Page 28 and 29: Problems 90151.time of 5.00 ms. Fin
- Page 30 and 31: “Neon lights,” commonly used in
- Page 32 and 33: 28.2 Atomic Spectra 905l(nm) 400 50
- Page 34 and 35: 28.3 The Bohr Theory of Hydrogen 90
- Page 36 and 37: 28.3 Th Bohr Theory of Hydrogen 909
- Page 38 and 39: 28.4 Modification of the Bohr Theor
- Page 40 and 41: 28.6 Quantum Mechanics and the Hydr
- Page 42 and 43: 28.7 The Spin Magnetic Quantum Numb
- Page 44 and 45: 28.9 The Exclusion Principle and th
- Page 46 and 47: 28.9 The Exclusion Principle and th
- Page 48 and 49: 28.11 Atomic Transitions 921electro
- Page 50 and 51: 28.12 Lasers and Holography 923is u
- Page 52 and 53: 28.13 Energy Bands in Solids 925Ene
- Page 54 and 55: 28.13 Energy Bands in Solids 927Ene
- Page 56 and 57: 28.14 Semiconductor Devices 929I (m
- Page 58 and 59: Summary 931(a)Figure 28.32 (a) Jack
- Page 60 and 61: Problems 9335. Is it possible for a
- Page 62 and 63: Problems 935tum number n. (e) Shoul
- Page 64 and 65: Problems 93748. A dimensionless num
- Page 66 and 67: Aerial view of a nuclear power plan
- Page 70 and 71: 29.2 Binding Energy 943130120110100
- Page 72 and 73: 29.3 Radioactivity 94529.3 RADIOACT
- Page 74 and 75: 29.3 Radioactivity 947INTERACTIVE E
- Page 76 and 77: 29.4 The Decay Processes 949Alpha D
- Page 78 and 79: 29.4 The Decay Processes 951Strateg
- Page 80 and 81: 29.4 The Decay Processes 953they we
- Page 82 and 83: 29.6 Nuclear Reactions 955wounds on
- Page 84 and 85: 29.6 Nuclear Reactions 957EXAMPLE 2
- Page 86 and 87: 29.7 Medical Applications of Radiat
- Page 88 and 89: 29.7 Medical Applications of Radiat
- Page 90 and 91: 29.8 Radiation Detectors 963Figure
- Page 92 and 93: Summary 965Photo Researchers, Inc./
- Page 94 and 95: Problems 967CONCEPTUAL QUESTIONS1.
- Page 96 and 97: Problems 96924. A building has beco
- Page 98 and 99: Problems 97157. A by-product of som
- Page 100 and 101: This photo shows scientist MelissaD
- Page 102 and 103: 30.1 Nuclear Fission 975Applying Ph
- Page 104 and 105: 30.2 Nuclear Reactors 977Courtesy o
- Page 106 and 107: 30.2 Nuclear Reactors 979events in
- Page 108 and 109: 30.3 Nuclear Fusion 981followed by
- Page 110 and 111: 30.3 Nuclear Fusion 983VacuumCurren
- Page 112 and 113: 30.6 Positrons and Other Antipartic
- Page 114 and 115: 30.7 Mesons and the Beginning of Pa
- Page 116 and 117: 30.9 Conservation Laws 989LeptonsLe
- Page 118 and 119:
30.10 Strange Particles and Strange
- Page 120 and 121:
30.12 Quarks 993n pΣ _ Σ 0 Σ + S
- Page 122 and 123:
30.12 Quarks 995charm C 1, its anti
- Page 124 and 125:
30.14 Electroweak Theory and the St
- Page 126 and 127:
30.15 The Cosmic Connection 999prot
- Page 128 and 129:
30.16 Problems and Perspectives 100
- Page 130 and 131:
Problems 100330.12 Quarks &30.13 Co
- Page 132 and 133:
Problems 1005particles fuse to prod
- Page 134 and 135:
Problems 100740. Assume binding ene
- Page 136 and 137:
A.1 MATHEMATICAL NOTATIONMany mathe
- Page 138 and 139:
A.3 Algebra A.3by 8, we have8x8 32
- Page 140 and 141:
A.3 Algebra A.5EXERCISESSolve the f
- Page 142 and 143:
A.5 Trigonometry A.7When natural lo
- Page 144 and 145:
APPENDIX BAn Abbreviated Table of I
- Page 146 and 147:
An Abbreviated Table of Isotopes A.
- Page 148 and 149:
An Abbreviated Table of Isotopes A.
- Page 150 and 151:
Some Useful Tables A.15TABLE C.3The
- Page 152 and 153:
Answers to Quick Quizzes,Odd-Number
- Page 154 and 155:
Answers to Quick Quizzes, Odd-Numbe
- Page 156 and 157:
Answers to Quick Quizzes, Odd-Numbe
- Page 158 and 159:
Answers to Quick Quizzes, Odd-Numbe
- Page 160 and 161:
Answers to Quick Quizzes, Odd-Numbe
- Page 162 and 163:
Answers to Quick Quizzes, Odd-Numbe
- Page 164 and 165:
Answers to Quick Quizzes, Odd-Numbe
- Page 166 and 167:
Answers to Quick Quizzes, Odd-Numbe
- Page 168 and 169:
IndexPage numbers followed by “f
- Page 170 and 171:
Current, 568-573, 586direction of,
- Page 172 and 173:
Index I.5Fissionnuclear, 973-976, 9
- Page 174 and 175:
Index I.7Magnetic field(s) (Continu
- Page 176 and 177:
Polarizer, 805-806, 805f, 806-807Po
- Page 178 and 179:
South poleEarth’s geographic, 626
- Page 180 and 181:
CreditsPhotographsThis page constit
- Page 182 and 183:
PEDAGOGICAL USE OF COLORDisplacemen
- Page 184 and 185:
PHYSICAL CONSTANTSQuantity Symbol V