Untitled - Malaysian Institute of Planners
Untitled - Malaysian Institute of Planners
Untitled - Malaysian Institute of Planners
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
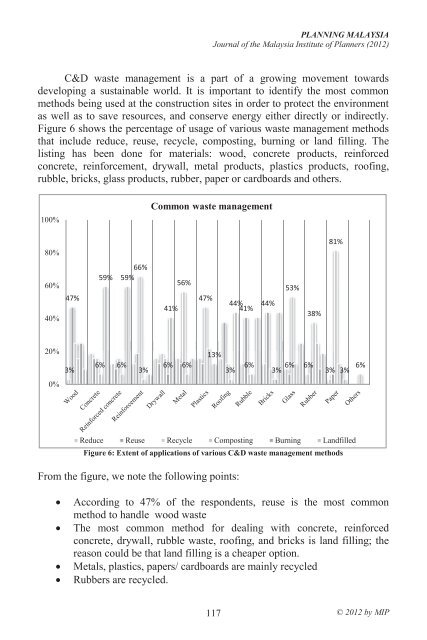
PLANNING MALAYSIAJournal <strong>of</strong> the Malaysia <strong>Institute</strong> <strong>of</strong> <strong>Planners</strong> (2012)C&D waste management is a part <strong>of</strong> a growing movement towardsdeveloping a sustainable world. It is important to identify the most commonmethods being used at the construction sites in order to protect the environmentas well as to save resources, and conserve energy either directly or indirectly.Figure 6 shows the percentage <strong>of</strong> usage <strong>of</strong> various waste management methodsthat include reduce, reuse, recycle, composting, burning or land filling. Thelisting has been done for materials: wood, concrete products, reinforcedconcrete, reinforcement, drywall, metal products, plastics products, ro<strong>of</strong>ing,rubble, bricks, glass products, rubber, paper or cardboards and others.100%Common waste management80%81%60%40%47%66%59% 59%41%56%47%44%53%38%20%3%6% 6%3%6%6%13%3%41% 44% 6%6%3%6%3%3%6%0%Reduce Reuse Recycle Composting Burning LandfilledFigure 6: Extent <strong>of</strong> applications <strong>of</strong> various C&D waste management methodsFrom the figure, we note the following points:According to 47% <strong>of</strong> the respondents, reuse is the most commonmethod to handle wood wasteThe most common method for dealing with concrete, reinforcedconcrete, drywall, rubble waste, ro<strong>of</strong>ing, and bricks is land filling; thereason could be that land filling is a cheaper option.Metals, plastics, papers/ cardboards are mainly recycledRubbers are recycled.117© 2012 by MIP